Veins and Arteries are the two different blood vessel types in the circulatory system.
These are mainly involved in blood circulation throughout the body. But the blood vessels, in terms of functioning, both are different from each other.
What are Arteries?
Arteries refer to the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart and branch to even smaller vessels.
Further, these smallest arteries, known as arterioles, are branched into the small capillaries where the nutrients, gases, and other waste molecules exchange is carried out.
What are Veins?
Veins are the blood vessels that are present throughout the body.
These are the tube-like translucent structures that perform the function of carrying out the deoxygenated blood from the tissues to the heart for the purpose of re-oxygenation.
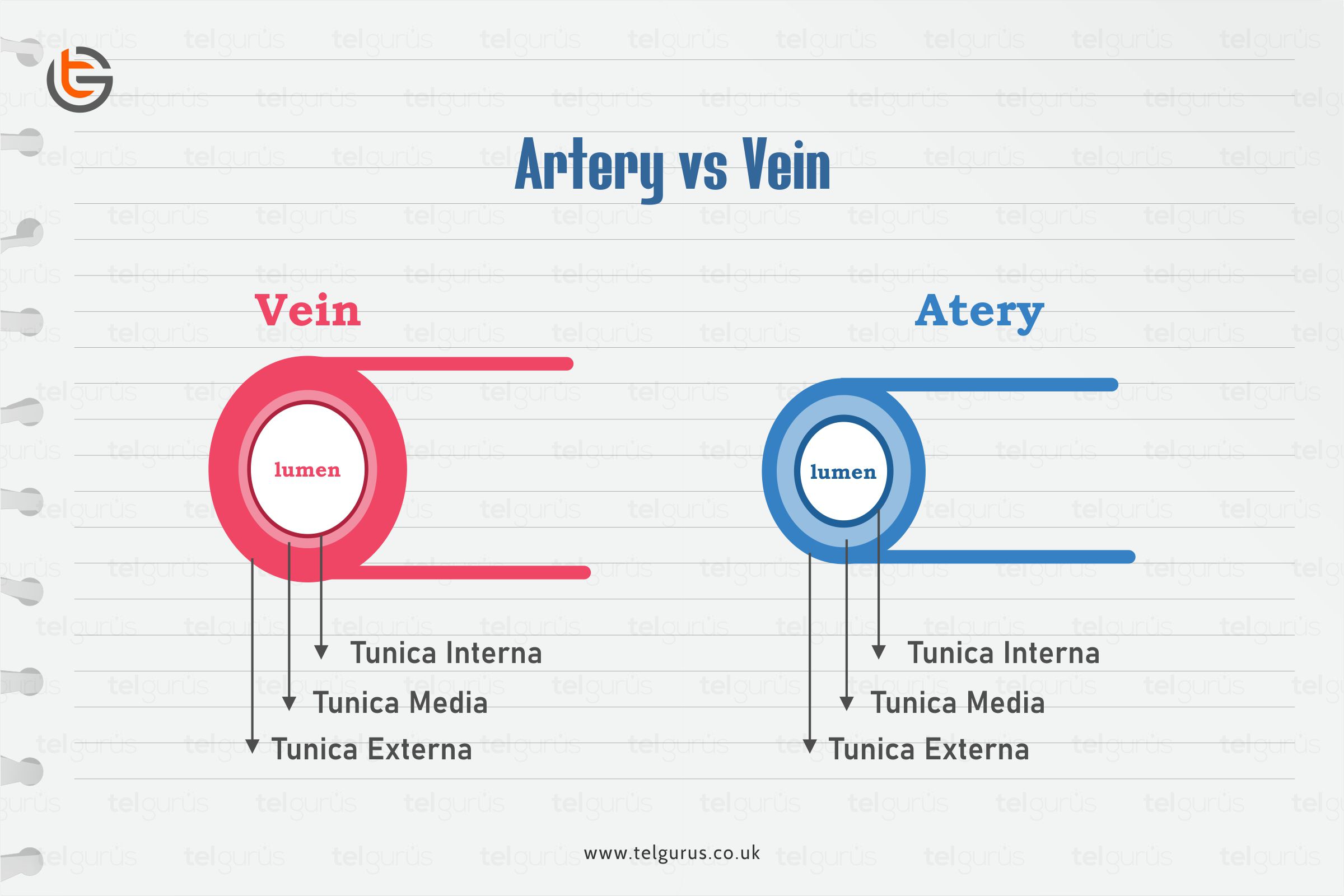
Two structural differences between Arteries and Veins
| Parameters | Arteries | Veins |
| Walls | Arteries have elastic, thick, and muscular walls | Veins have thin walls with a few elastic fibers. |
| Valves | Arteries do not have any valves | Veins have one-way valves |
Arteries require thick, muscular, and elastic walls to give them strength and elasticity to cope with the oxygenated blood’s high pressure surges coming from the heart.
The elasticity permits the walls to recoil back to the original shape after being augmented in diameter to allow the blood through the surge.
Veins require valves because the blood flowing through them at low pressures further necessitates something to prevent it from going backward.
They are necessary in order to avoid blood pooling. Arteries do not require valves as the blood flows at high pressures where it cannot go backward.
Other differences between Arteries and Veins
| Parameters | Arteries | Veins |
| Functions | Arteries are involved in carrying the oxygenated blood except for pulmonary arteries | Veins are involved in carrying deoxygenated blood except for pulmonary veins |
| Position | These are located deep within the body | These are peripherally located closer to the skin |
| Walls | These consist of three layers that are highly muscular, rigid, and thicker. | These consist of three distinct layers that are less muscular and thinner |
| Appearance | These are red | These are blue |
| Pressure rate | High pressure as the blood flows by pumping heart pressure | Low pressure as the blood flows by the veins’ capillary action |
| Transports | Arteries carry blood away from the heart to several parts of the body | Veins carry blood towards the heart from several parts of the body |
| Disorders | Arteries are generally at a greater risk of specific diseases like atherosclerosis etc | Veins are generally less susceptible to the diseases like varicose veins |
| Lumen | Here Lumen is narrow | Here Lumen is wide |
| Oxygen Level | The oxygen level is comparatively high | The oxygen level is comparatively low |
| Blood flow direction | The blood flow direction of arteries is in the downward direction from the heart to the blood tissues. | The blood flow direction is in the upward direction from the body tissues to the heart. |
| Carbon Dioxide Level | The carbon dioxide level is low | The carbon dioxide level is high |
| Valves | Here valves are absent | Here valves are present. |
Bottom Line!
The major structural differences between the arteries and veins include:
- Arteries have thick, elastic and muscular walls, whereas veins have thin walls with a few elastic fibers.
- Arteries do not have any walls, whereas veins have one-way valves.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development