Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
Explain the mechanism of breathing.
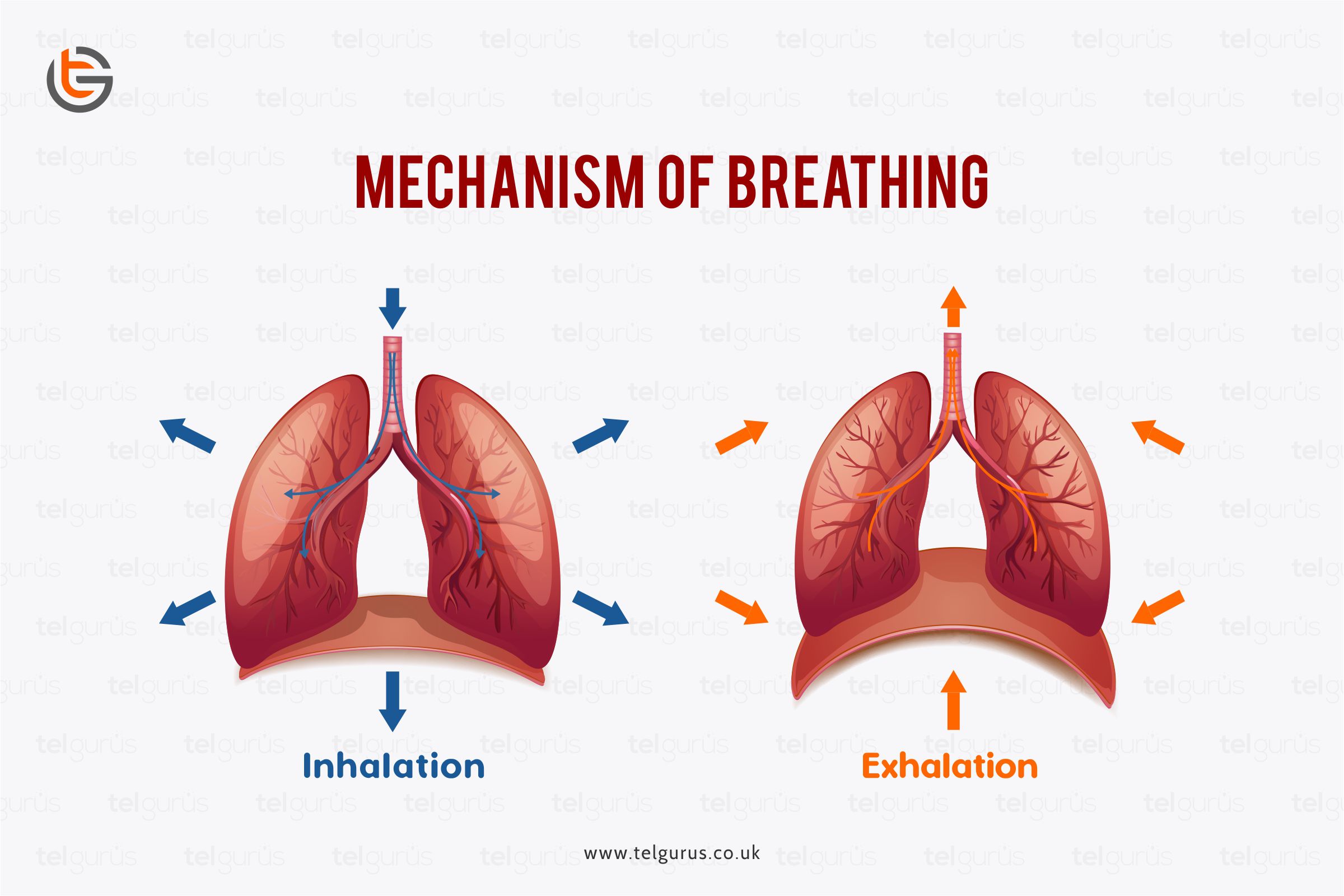
The action of breathing out and in is due to the pressure changes within the thorax compared to the outside. The breathing mechanism generally involves ample organs and two processes.
Let us get acquainted with everything you need to know about the breathing mechanism.
What is breathing?
Breathing refers to a process in which the air moves in and out of the lungs. This process is generally carried out through several respiratory organs.
In short, breathing refers to the simple give and take process.
Whenever we breathe in, we take in the air that is rich in oxygen from the atmosphere. In the return of this intake process, we give out the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that the plants further utilize for the photosynthesis process.
Breathing is basically a continuous process that goes on throughout the life of an organism.
The process of in-taking the oxygen-rich air is known as inhalation, whereas the process of giving out the air rich in Carbon Dioxide is called exhalation.
Daily a person breathes ample time, and the breathing rate generally depends on the person’s activity. The breathing rate usually rises when a person is running, brisk walking, or after some heavy exercises, and on the contrary, the rate decreases when the person is calm.
An adult’s breathing rate is 15-18 times per minute, and during heavy exercises, the breathing rate exceeds 25 breaths per minute.
Breathing Mechanism
The air that we breathe in and out generally varies in its pressure. So, fundamentally when there is a fall in the air pressure, the alveolar spaces also fall, and the air enters the lungs, known as the inspiration of the air.
And as the alveoli’s pressure exceeds the atmospheric pressure, the air gets blown out from the lungs, known as expiration.
The air’s flow rate is in proportion to the pressure difference’s magnitude. And a mechanism of breathing generally involves two processes.
- Inspiration
- Expiration
Inspiration
In the inspiration process, a muscle contraction attached to the ribs in the outer side would pull the ribs, resulting in the chest cavity expansion.
After this, the diaphragm contracts while moving downwards and expands the chest cavity resulting in the abdominal muscles contraction.
The chest cavity expansion then leads to the production of a partial vacuum that sucks the air into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli.
Inspiration mechanism
- The intake process of atmospheric air is an active process that is referred to as inspiration.
- When the thoracic cavity’s volume increases and air pressure decreases, the inspiration process takes place.
- The external intercostal muscles contraction then increases the thoracic cavity’s volume.
- The diaphragm contraction further augments the size of the thoracic activity. Concurrently, the lungs expand.
- With the lungs expansion, the air pressure within the lungs decreases
- The pressure equalizes, and the atmospheric air rushes into the lungs.
Expiration
After the gaseous exchange takes place in the lungs and the air is barred out, the process is known as the expiration process. Basically, this air expulsion is known as expiration.
During the expiration process, the muscles attached to the ribs contract.
The diaphragm muscles and abdomen relax, leading to a decrease in chest cavity volume and augments the lungs pressure, leading to the air present in the lungs to be pushed out with the help of the nose.
Expiration Mechanism
- The exhaling carbon dioxide process is a passive process that is known as expiration.
- It takes place when the thoracic activity size decreases and outside air pressure increases.
- The external intercostal muscles relax, and the internal intercostal muscles contract.
- Consequently, the ribs are pulled inwards and the thoracic cavity size reduces.
- The diaphragm is then relaxed, and the lungs get compressed.
- As a result, the pressure increases, and the air is pulled outside.
Bottom Line!
Breathing is a process of inhaling (O2) Oxygen and exhaling (CO2) Carbon dioxide by the lungs, and there is a proper system of organs that are involved in the process of breathing. We hope this answer helped you understand the entire concept of the breathing mechanism.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?