Noble gases are unreactive non-metal gases that often show trends in their physical properties, and their uses depend upon their low density, inertness, and non-inflammability.
Let us get acquainted with everything you need to know about noble gases and the reason behind the query.
What are noble gases?
Noble gases refer to the chemical elements in periodic table’s group 18.
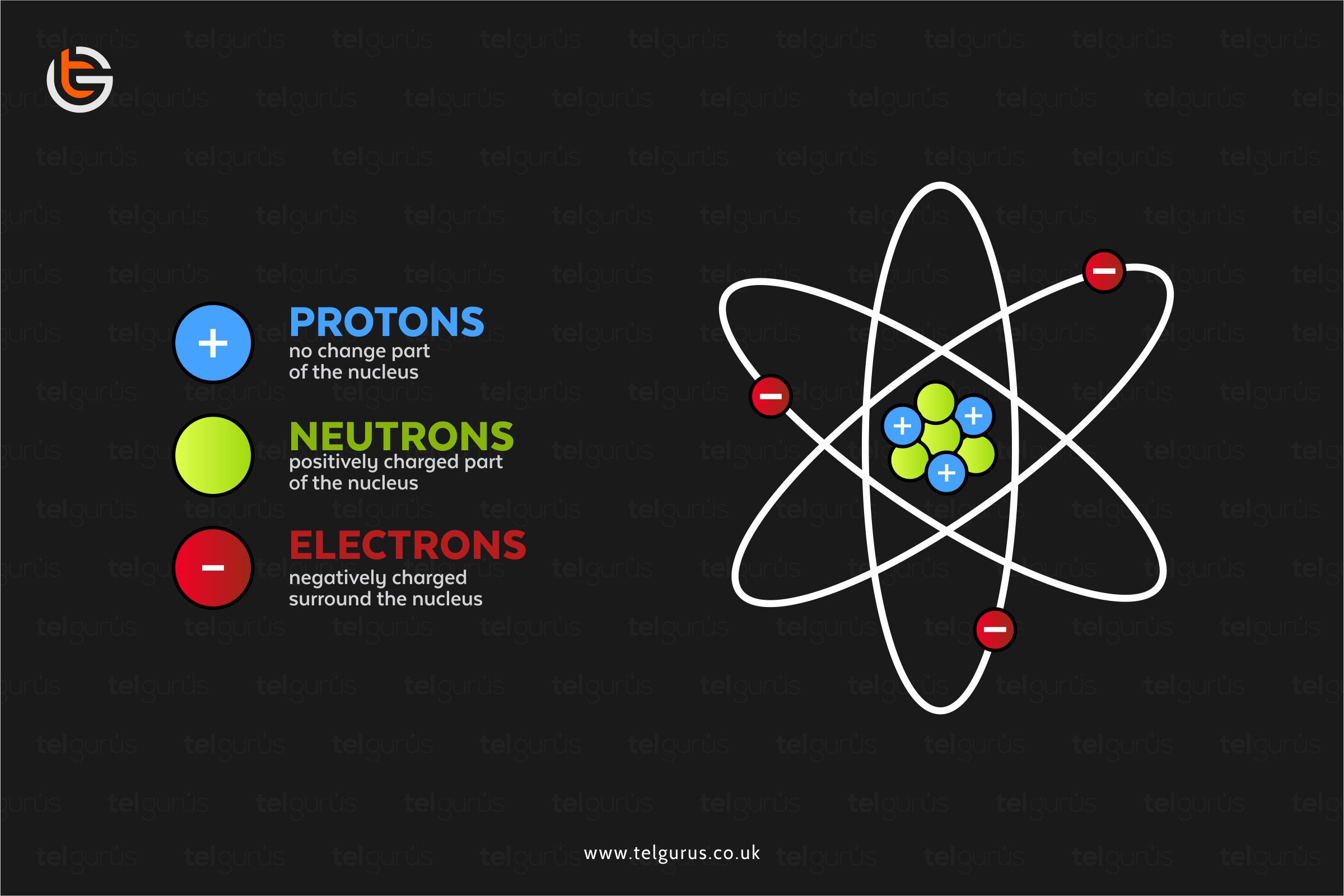
The noble gases are most stable because of the maximum number of valence electrons in their outermost shell. And that is why they rarely react with other elements as they are already stable.
Chemical properties of Noble Gases
As compared to the other elements on the periodic table, noble gases are inert and highly unreactive.
Uses and properties of noble gases
The primary properties of the noble gases include
- Lower densities
- Inert
- Not flammable
Uses of Noble gases
- Helium
Helium is utilized as a lifting gas in airships and party balloons.
- It’s non-flammable, so it cannot be set on fire.
- It’s less dense than air do the airships and balloons rise
- Argon
Argon is often utilized as a shielding gas while welding the metal pieces together.
- It is denser than air, so it prevents the air from getting into the metal
- It’s inert so that hot metal cannot spoil the weld and oxidize it.
So why are noble gases unreactive?
Noble gases are so unreactive because of the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of their atoms. And as their outer shell is full, indicating it is complicated for them to take or give electrons.
As the noble gases enclose an entire valence shell of electrons and due to this configuration, they are
- Difficult to oxidize as the valence electrons are firmly held by nuclear charge.
- Difficult to diminish as the electrons must enter the next valence shell.
Understanding with explanation!
Noble gases’ outer shell of the valence electrons is generally considered full, giving them a slight tendency to participate in chemical reactions.
The boiling and melting points for a noble gas are close together, differing by less than 18 degrees Fahrenheit or 10 degrees Celsius, including the liquids over a smaller temperature range.
The noble gases generally show significantly lower chemical reactivity, and as an outcome, only a few hundred noble gases compounds are formed.
Neutral compounds in which neon and helium are included in the chemical bonding have not been formed. On the contrary, the krypton, argon, and xenon show minor reactivity only.
Therefore, the reactivity follows the order
Ne < He < Ar < Kr < Xe < Rn
Bottom Line!
Noble gases are considered so unreactive as they have a fully filled outermost orbital configuration, and because of which noble gases are very much stable and have minimum energy.
Read More – Chemistry Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development