Mitochondria refer to the membrane-bound organelles that are present in the eukaryotic cell’s cytoplasm, which produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is the primary energy molecule utilized by the cells.
While talking about mitochondria, it is essential to get familiar with everything concerning it. Let us begin with the definition first.
What are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are well known by the name “powerhouse of the cell”. These are the double membrane-bound organelle that is usually found in most eukaryotic organisms inside the cytoplasm and essentially work as a cell’s digestive system.
Mitochondria play a crucial role in breaking down the nutrients while generating energy-rich molecules for the cells. Several biochemical reactions involved in cellular respiration occur within the mitochondria.
The term mitochondrion is derived from the Greek words namely “mitos” and “chondrion”, which means thread and granules like respectively.
Why is Mitochondria known as the powerhouse of the cell?
It is because these are the cell’s organelles that are further responsible for producing ATP and the energy currency of the cell.
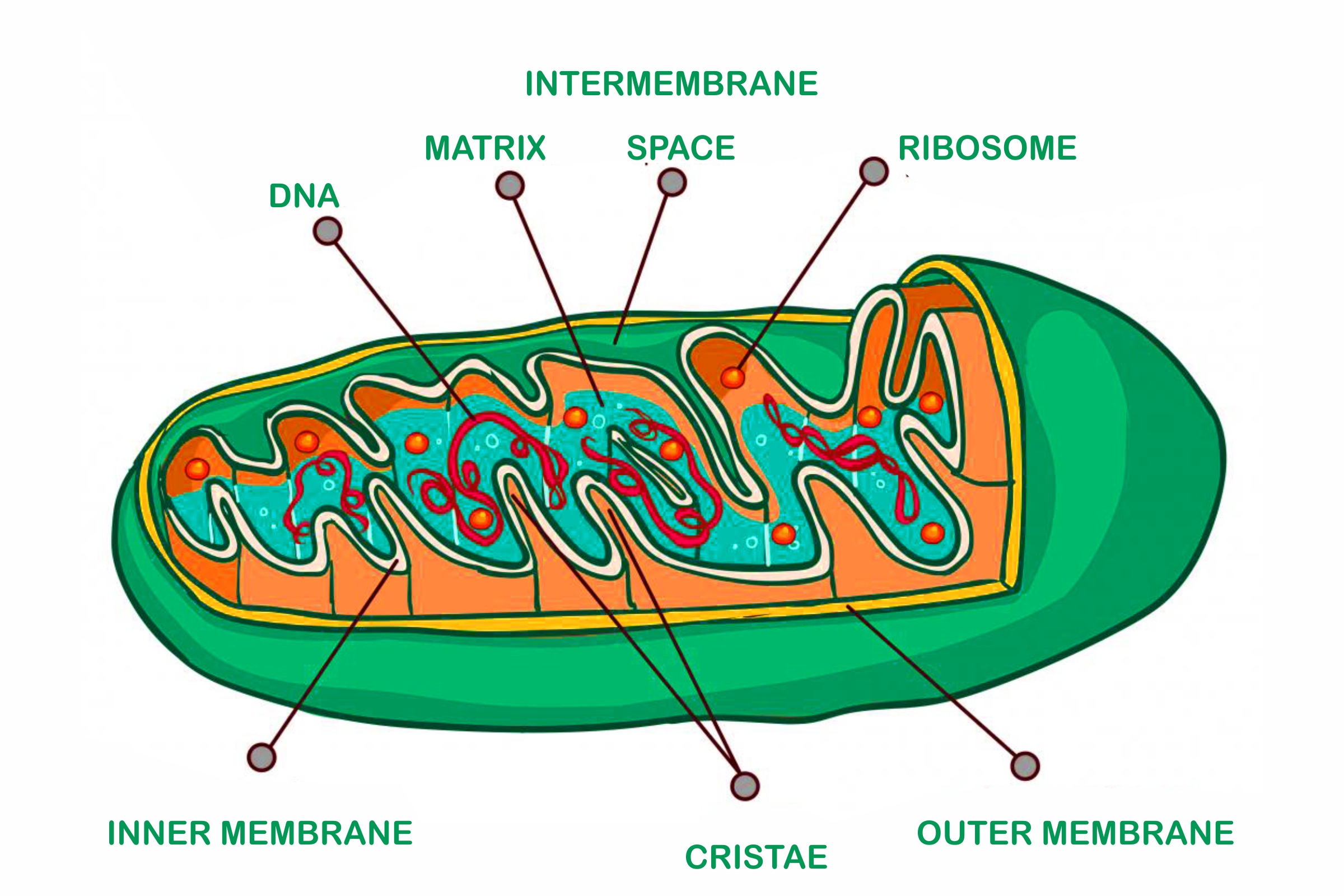
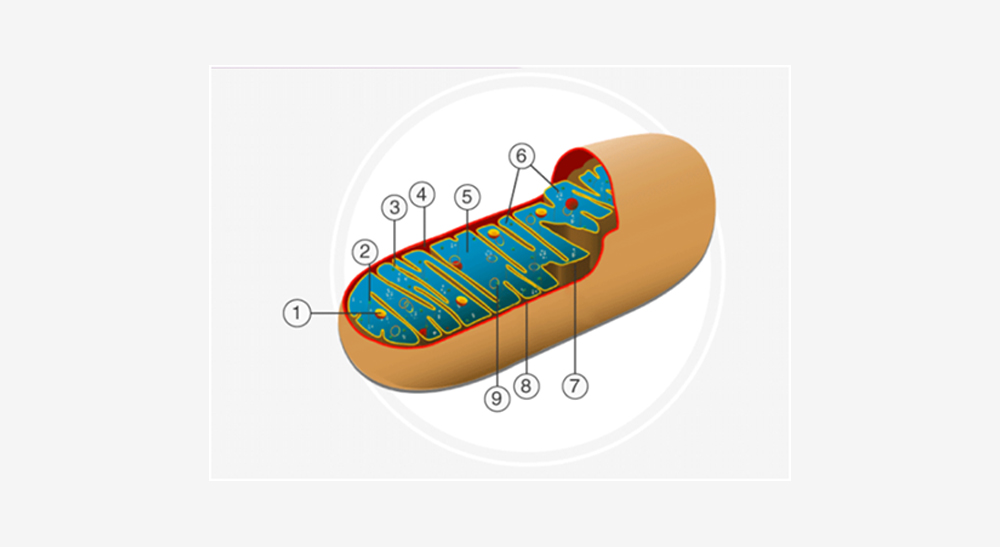
Structure of Mitochondria
Here in the diagram, the points mentioned refers to
- 1 for granules
- 2 for ribosomes
- 3 for Cristae
- 4 for Inter membrane space
- 5 for Matrix
- 6 for ATP Synthase Particle
- 7 for Inner membrane
- 8 for Outer Membrane
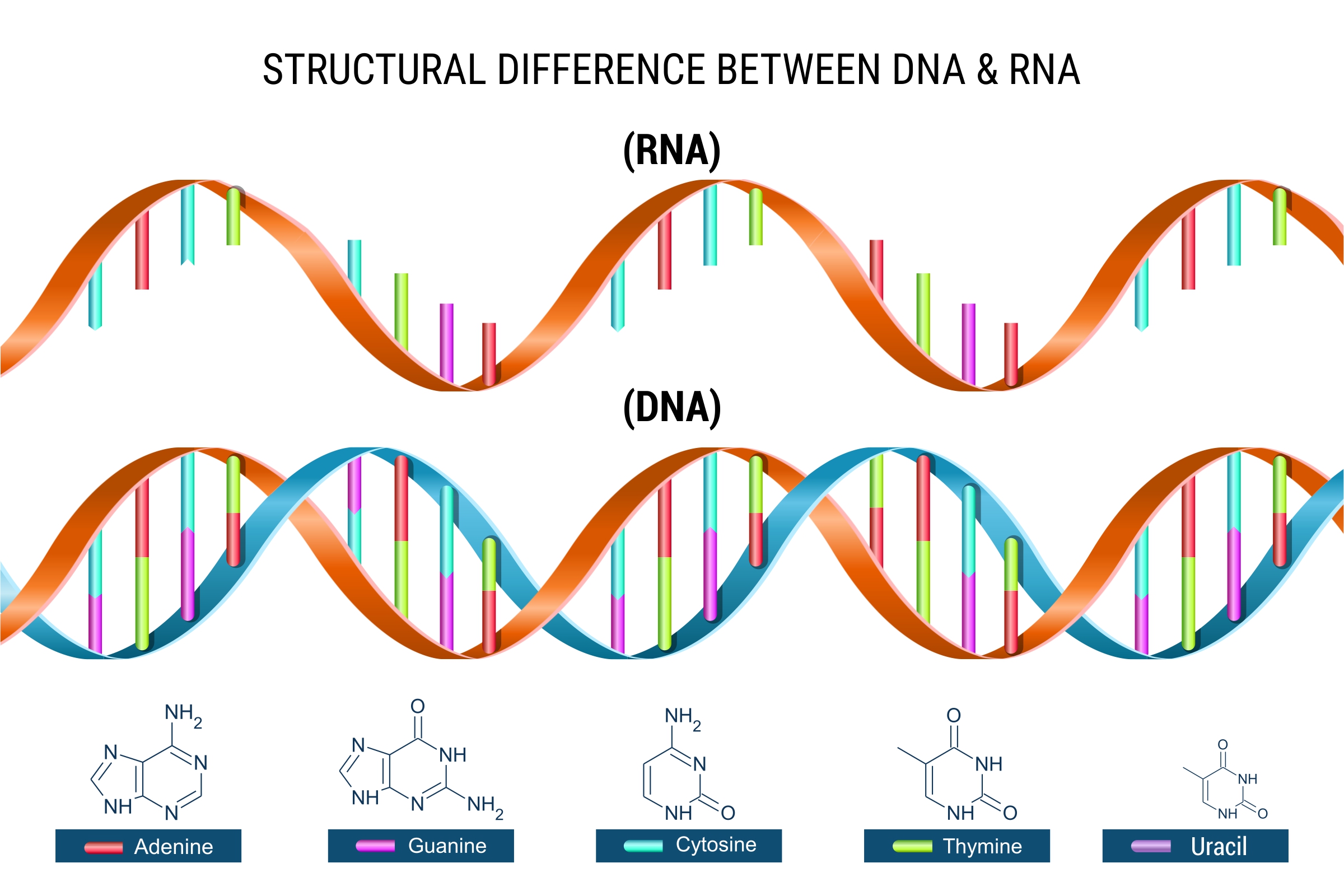
- 9 for Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
While talking about the structure of mitochondria, it has a double membrane and a rod-shaped structure that is found in both animal and plant cells.
- Its size ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometre in diameter.
- Its structure includes an inner membrane, an outer membrane, and a get-like material known as a matrix.
- Its inner and outer membrane are comprised of proteins and phospholipid layers separated by intermembrane spaces.
- The outer membrane covers the mitochondrion’s surface and has a large number of porins that are unique proteins.
- It is freely permeable to nutrients, molecules, ions, AP molecules, and energy molecules like ADP.
Mitochondria Functions
An essential function of mitochondria is to produce energy via the oxidative phosphorylation process. However, apart from this important function, it is also involved in the following processes.
- It regulates a cell’s metabolic activity
- It promotes the cell multiplication and growth of new cells.
- It plays an essential role in programmed cell death or apoptosis.
- It helps in detoxifying the ammonia in the liver cells.
- It is also responsible for building specific parts of the blood and several hormones like oestrogen and testosterone.
- It facilitates in maintaining the calcium ions adequate concentration with several compartments of the cell.
- It is also involved in several cellular activities like cell signalling, cellular differentiation, cell senescence, cell growth, and controlling the cell cycle.
However, any irregularity in mitochondria functioning can directly affect human health, but it is challenging to identify that as symptoms may vary from person to person. And the disorders can be pretty severe in several cases that it can even lead to causing the organ to fail. Several mitochondrial disorders include Barth syndrome, Alpers diseases, Kearns Sayre Syndrome.