Diffusion is the process of molecules’ movement under a concentration gradient. It is an essential process occurring in all living beings and helps in substances’ movement in and out of the cells.
Gases and liquids undergo the diffusion process as the molecules can move randomly.
What is Diffusion?
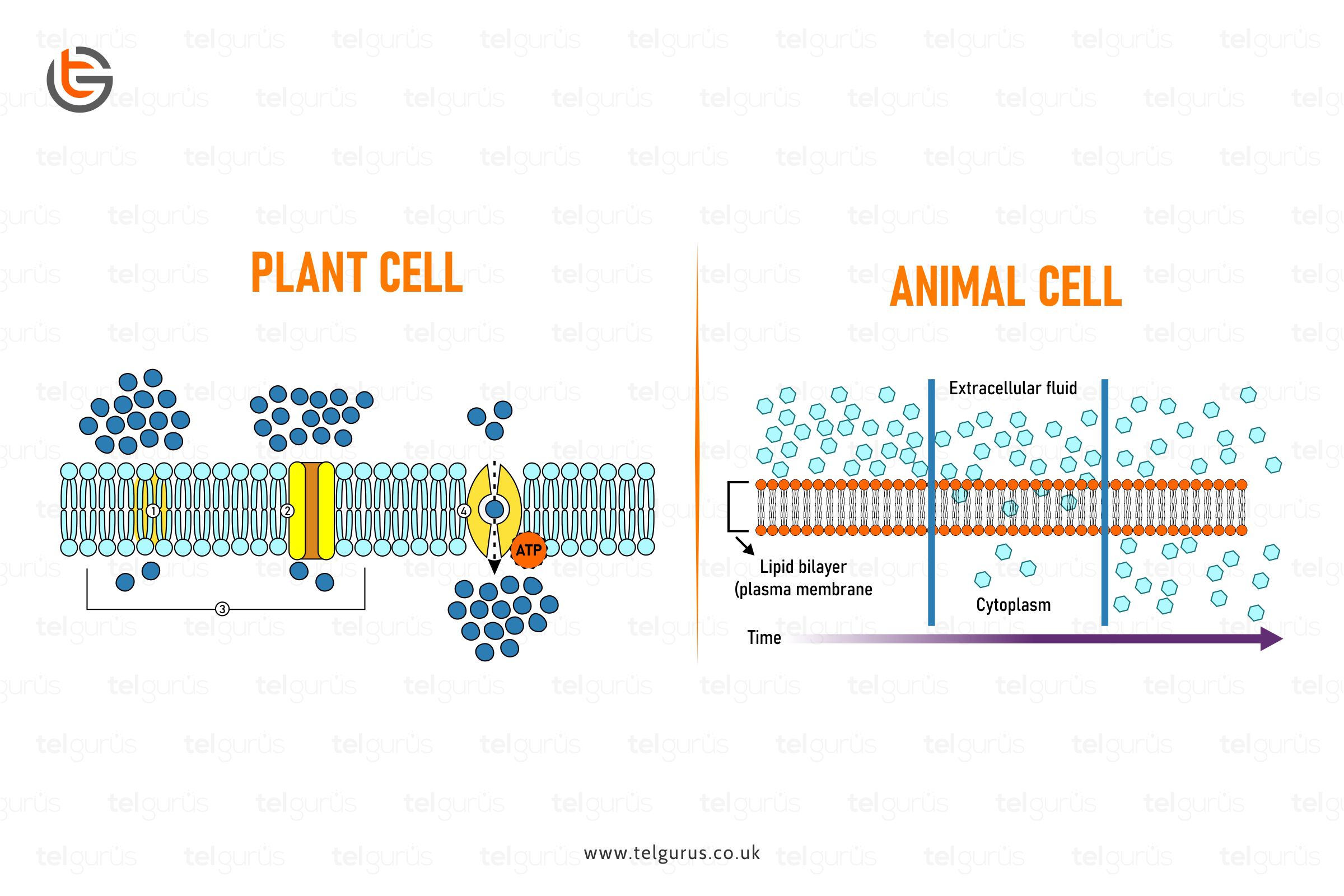
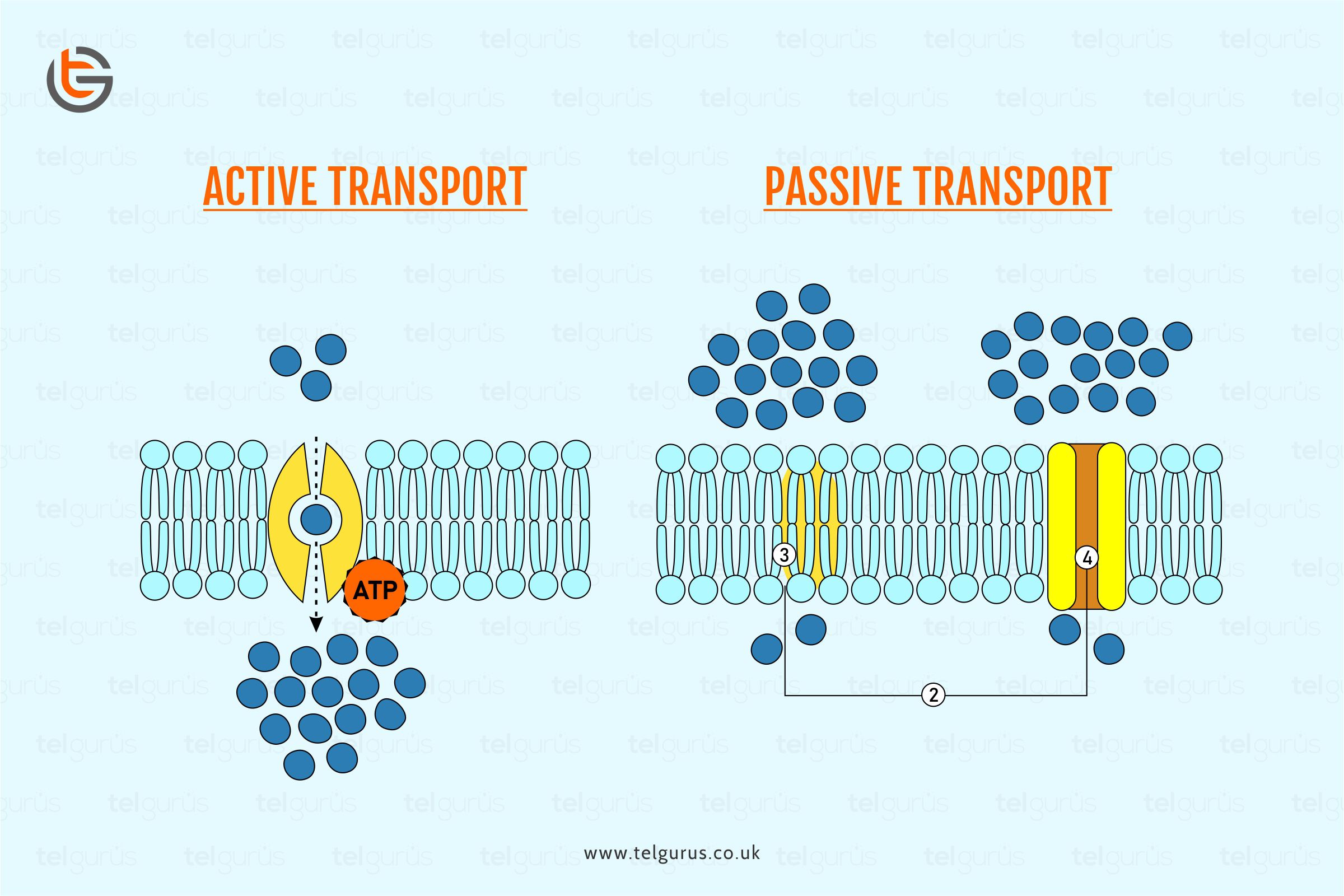
Diffusion is a passive process involving the molecule’s movement from a higher concentration region to a lower concentration. Here the term passive indicates the process that doesn’t need any energy input to occur.
Diffusion can take place across partially permeable membranes like surrounding cells. Therefore the diffusion process is involved in the essential molecules moving into and out of the cells.
It is crucial for the substance uptake required by the cells and also in the waste products removal generated by the cells.
Types of Diffusion
The diffusion process is classified into two types. This includes:
- Simple Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
Simple Diffusion is when the substance moves via a semi-permeable membrane or a solution devoid of any help from the transport proteins.
For instance, bacteria deliver small nutrients, oxygen, and water into the cytoplasm via simple Diffusion.
Facilitated Diffusion is a process of a molecule’s passive movement across the cell membrane from a higher concentration region to the lower concentration region through the carrier molecule.
Factors affecting diffusion process
Several factors are affecting the diffusion process. These factors include:
- Interaction area
- Temperature
- Particle’s size
- Concentration gradient’s steepness
Diffusion Examples
A few examples of Diffusion include:
- A perfuming spray or a room freshener that gets diffused into the air through which we can sense the odor.
- Sugar gets dissolved evenly in the water, devoid of having to stir it.
Importance of Diffusion in animals
Glucose and oxygen react to generate water along with ATP and carbon dioxide in the aerobic respiration process.
Therefore the glucose and oxygen must be taken by the cells, and generally, the concentration of such molecules outside the cell is higher as compared to inside.
Consequently, the overall net movement of such molecules will be down the concentration gradient, and then they will move to the cell through Diffusion.
Similarly, the CO2 generated is a waste product that moves out of the cell and again through Diffusion down its concentration gradient.
In short, in the case of animals, the diffusion process is essential for the respiration process.
Importance of Diffusion in plants
Useful minerals and ions require to be taken up from the soil into the plants through their root hair cells. These cells are then adapted to maximize the diffusion rate.
Consequently, the useful molecules present in the soil move down a concentration gradient and then into the roots to be taken by the plant.
Several molecules found in the soil are essential for the development and survival of plants while making Diffusion an essential process.
In short, in the case of the plant’s Diffusion is essential for the mineral uptake process.
Bottom Line!
The diffusion process in animals is essential for respiration. On the contrary, it is used for mineral uptake in the case of plants.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development