Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is the difference between diffusion and active transport?
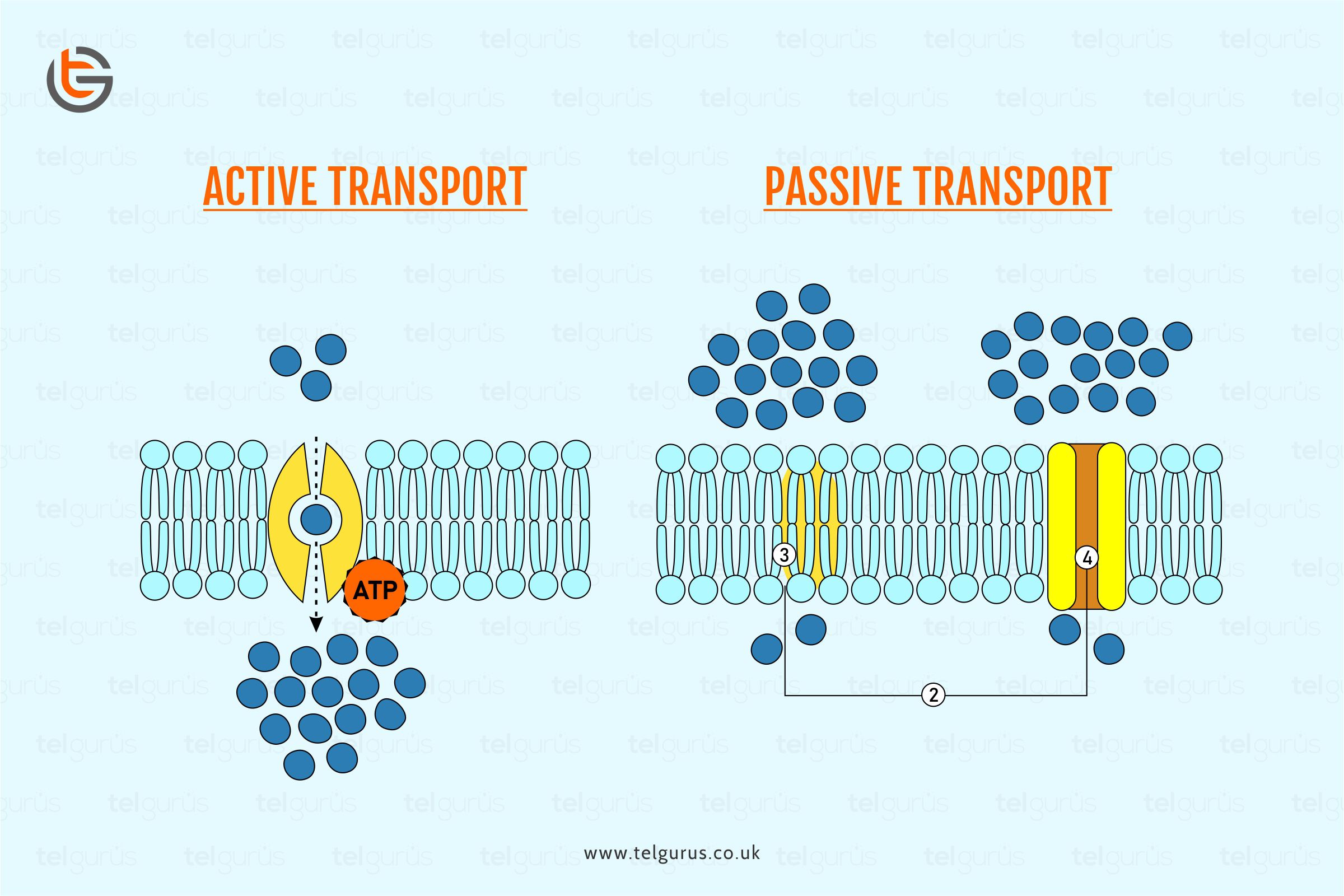
Active transport and diffusion are the two types of methods involved in the movement of the molecules across the cell membrane. The cell membrane serves as a semi-permeable barrier to the molecules that pass through it.
The primary difference between active transport and diffusion is that active transport needs cellular energy to transport the molecules against the concentration gradient.
In contrast, diffusion refers to the passive transport method where the molecules move across the cell membrane through a concentration gradient.
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is a molecule’s passive movement along with the concentration of a higher one to a lower one. The diffusion methods are further categorized into three, including simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis.
What is active transport?
Active transport refers to the particle’s movement across the cell membrane from lower concentration to higher concentrations using metallic energy.
Active transport gets assistance from the enzymes bound to the metabolic energy and cellular membranes in the form of ATP.
The primary and secondary transports are the further two types of active transport processes.
Similarities between Diffusion and Active Transport
Both active transport and diffusion permit a cell to maintain homeostasis in the cell transporting the molecules across the cell membrane.
Molecular transportation takes place with the transmembrane proteins’ assistance other than diffusion.
Difference between Active Transport and Diffusion
| Parameters | Active Transport | Diffusion |
| Definition | It refers to the particle’s movements across a cellular membrane from a low concentration to a higher one by using metabolic energy. | It refers to the molecule’s passive movement along a concentration gradient of higher concentration to lower one. |
| Concentration gradient | It occurs against a concentration gradient | It occurs through a concentration gradient |
| Metabolic energy | It requires metabolic energy in ATP’s form for the molecule’s transportation across the cell membrane. | It doesn’t require metabolic energy to transport molecules across the cell membrane. |
| Equilibrium | No molecules equilibrium is established here | No net molecules movement is observed after the equilibrium establishment on either side of the membrane. |
| Types of particles | Ions, proteins, large cells, and complex sugars are transported through the cell membrane | Carbon dioxide, water, sex hormones, small monosaccharides, oxygen, and other smaller hydrophobic molecules are transported through the cell membrane. |
| Function | It allows the molecules transportation like wastes and nutrients against the concentration gradient | It maintains a dynamic equilibrium of nutrients, gases, wastes, and water in and out of the cell. |
| Examples | · Secretion of a substance into the bloodstream
· Plants take up nutrients from the soil · Potassium or sodium pump · Endocytosis · Exocytosis |
· Diffusion of molecules from the blood to the cells
· Oxygen moving from airways |
Bottom Line!
Active transport and diffusion are the two molecule transporting methods across the cell membrane.
Diffusion is a passive process, whereas active transport requires the metabolic energy for the molecule’s transportation across the cell membrane. The primary difference between both the terms is their energy requirements for the molecule’s transportation across the cell membrane.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?