Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
Describe the process of transcription?
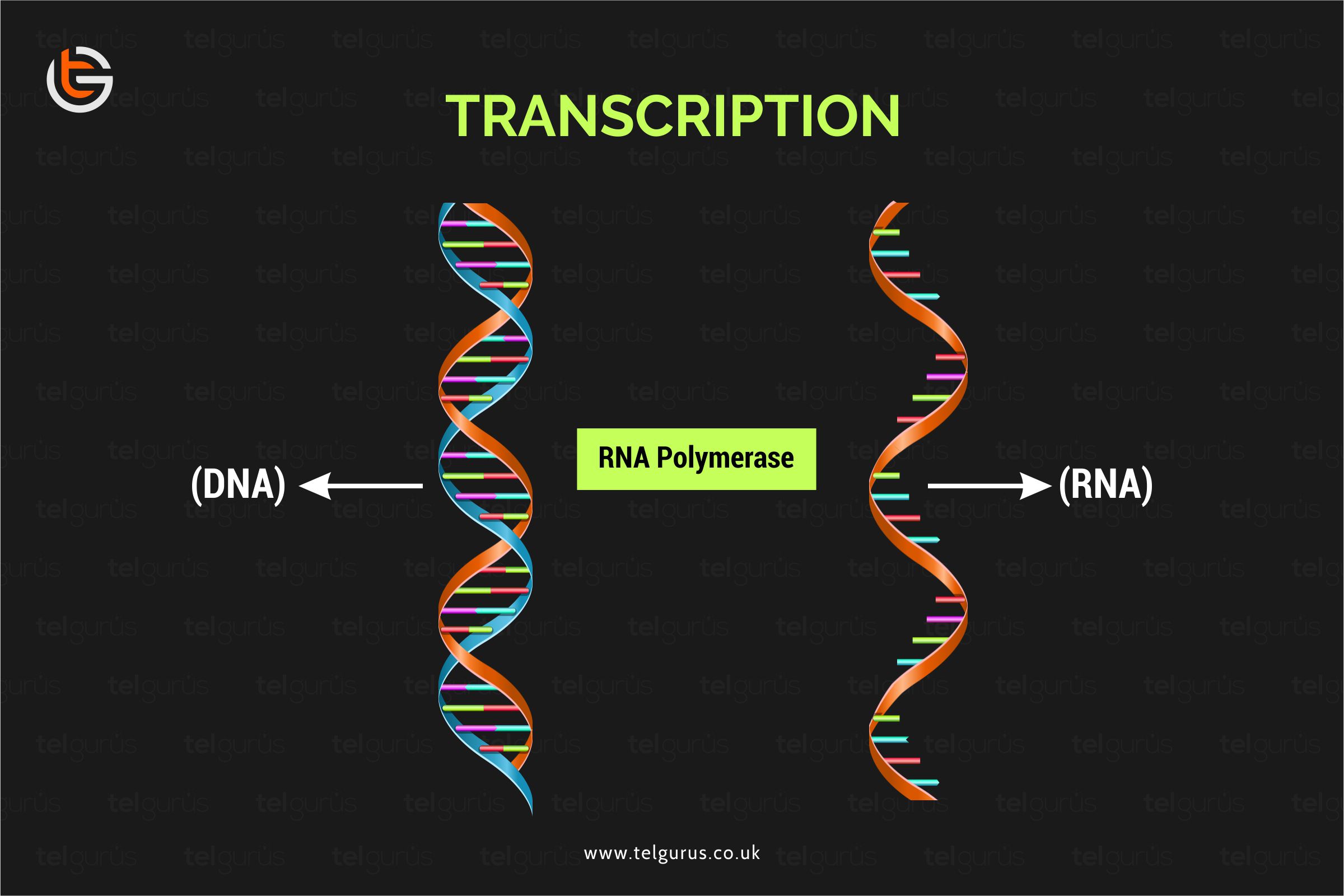
Transcription is the initial step of the gene expression that entails the RNA molecule formation from DNA. Let us get acquainted with everything you need to know about it.
What is transcription?
Transcription refers to the process of copying the information in a DNA strand into a new molecule of messenger RNA.
The transcription process!
The transcription process refers to the transcribing of DNA code into another code type or message. An enzyme known as the RNA polymerase binds to the DNA sequence’s specific part known as a promoter.
Then the DNA must unwind and unzip to expose the DNA’s two strands.
Here one strand contains bases complementary to genes requiring to be transcribed acting as a template through the complementary bases pairing and nucleotides alongside the template strands leading to the formation of a single-stranded mRNA molecule.
Whenever the RNA polymerase identifies that it has reached a stop codon or a terminator sequence referring to the end of the sequence coding, the mRNA detached from DNA.
The DNA then rewinds behind the RNA polymerase because it moves along across the DNA strand.
After that, the mRNA molecule moves out of the nucleus through a nuclear prone into the cytoplasm, ready to be translated into protein at the ribosome’s site.
Transcription Stages
The DNA transcription process is divided into three main stages, including
Stage 1- Initiation
Transcription is a process catalyzed by the RNA polymerase that attaches and moves along the DNA molecule until it identifies the promoter sequence. This DNA’s area marks the starting point of the transcription process.
The transcription factors are the proteins that control the transcription rate and bind to the promoter sequences with RNA polymerase.
Once it gets bound to the promoter sequence, the RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA’s double helix portion while exposing the bases on both the DNA strands.
Stage- 2 Elongation
During the elongation process, one DNA strand is read in the direction of 3’ to 5’ and endows with the template for a new mRNA molecule.
The other DNA strand is considered the coding strand due to its base sequence that is identical to the synthesized mRNA.
RNA polymerase then utilizes the incoming ribonucleotides to generate the new mRNA strand.
And it does this by catalyzing the phosphodiester bonds’ formation between adjacent nucleotides while utilizing the complementary base pairings.
The complementary base pairing means pairing A to U, C to G, G to C, and T to A. The bases can be added to 3 prime ends only, which is why the strand elongates into 3’ direction.
Stage- 3 Termination
The elongation process continues till the RNA polymerase encounters a stop sequence. At this stage, the transcription process stops, and the RNA polymerase liberates the DNA template.
Bottom Line!
DNA transcription refers to the process through which the genetic information contained within the DNA is rewritten into mRNA by RNA polymerase. This rewritten mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as a basis for DNA translation.
We hope that the process mentioned above and the explanation helped you understand the concept well.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?