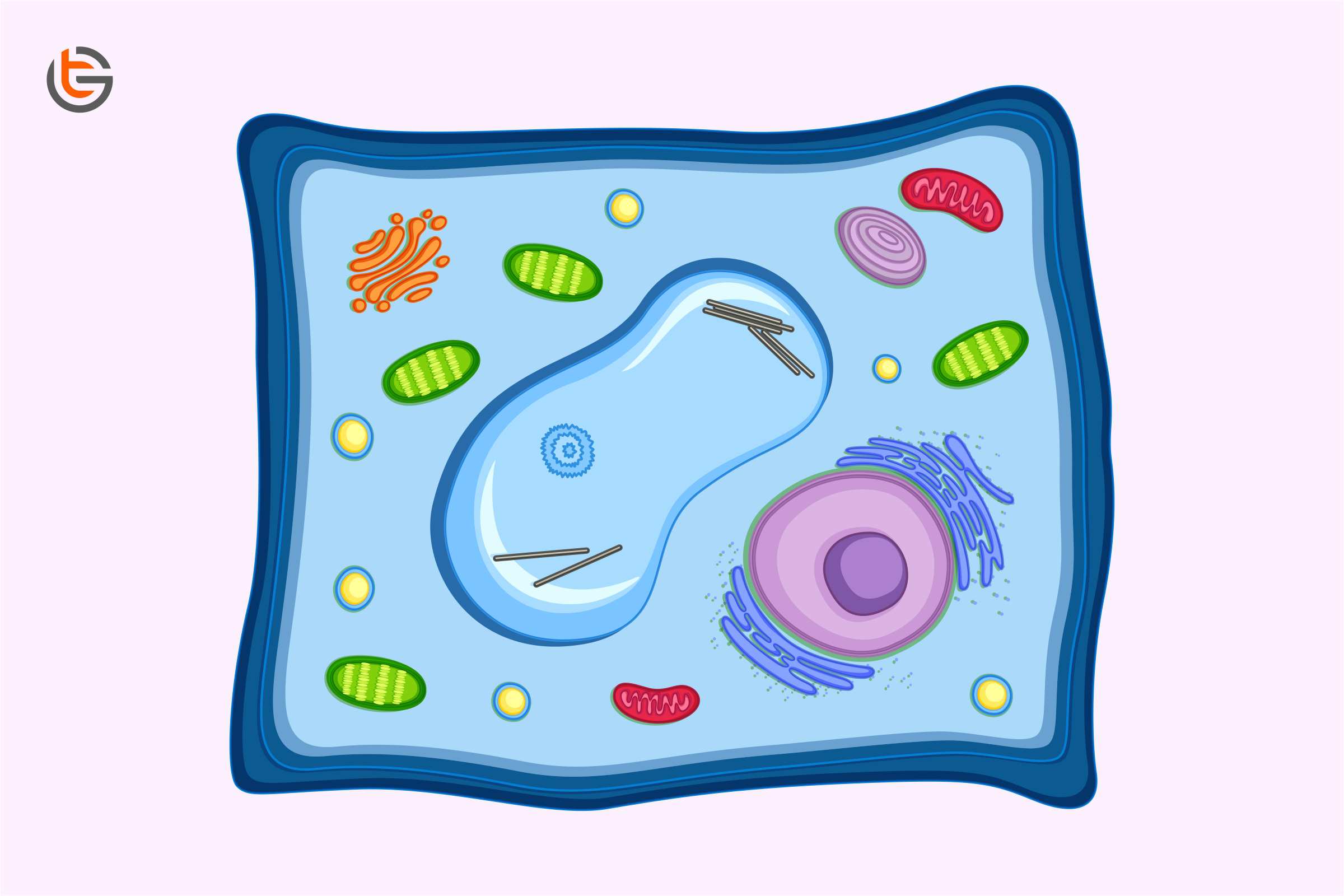
Plant cells have chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, a large central vacuole, cell wall, and plastids, whereas animal cells do not. Talking about animal cells, they have lysosomes and centrosomes.
Let us get familiar with the detailed discussion on three cell structures that plant cells have, but animal cells do not.
1. The Cell Wall
The cell wall endows with extra support and strength for the plant cell, so it does not get burst while gaining water by the endosmosis process.
In a plant cell, a structure to the plasma membrane is known as the cell wall. A cell wall is rigid covering protection for the cell and provides them with structural support. It also gives the shape to the cell.
Some protest cells and fungal cells also have cell walls. For instance, in the case of cellulose, while the main component of a prokaryotic cell wall is peptidoglycan, the primary organic molecule in the plant’s cell wall is cellulose. A polysaccharide is made up of a solid and long chain of glucose units. Whenever the nutritional information refers to dietary fiber it is, in turn, referring to the cellulose food content.
2. Chloroplasts
Chloroplast is the place where the process of photosynthesis occurs. Chloroplasts have their own ribosomes and DNA. Chloroplasts can be found in photoautotrophic eukaryotic cells like algae and plants. It functions in the photosynthesis process.
In the photosynthesis process, water, light energy, and carbon dioxide are used to make oxygen and glucose. This is the significant difference between animals and plants that plants make their own food while animals rely on other organisms.
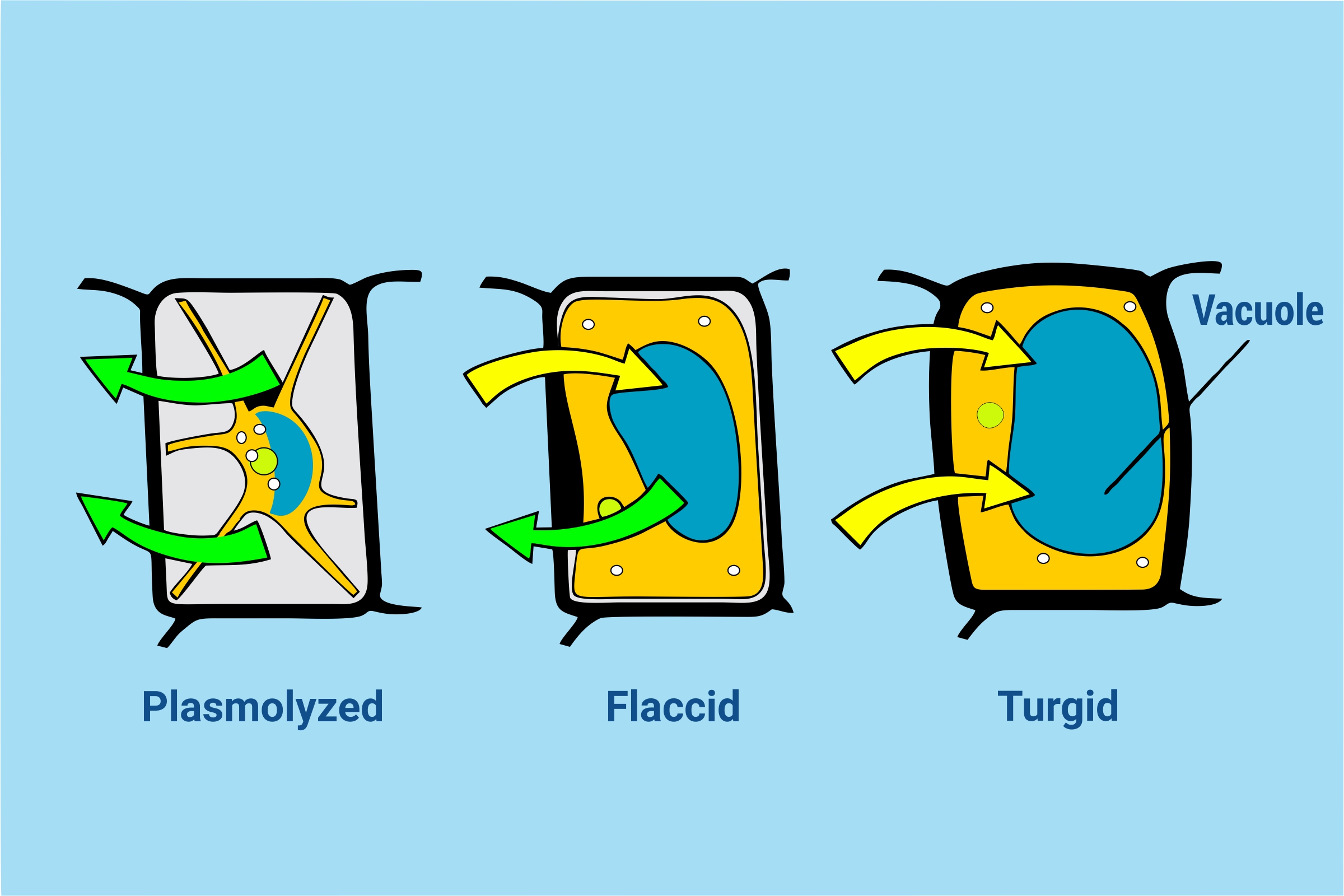
3. Large permanent Vacuole
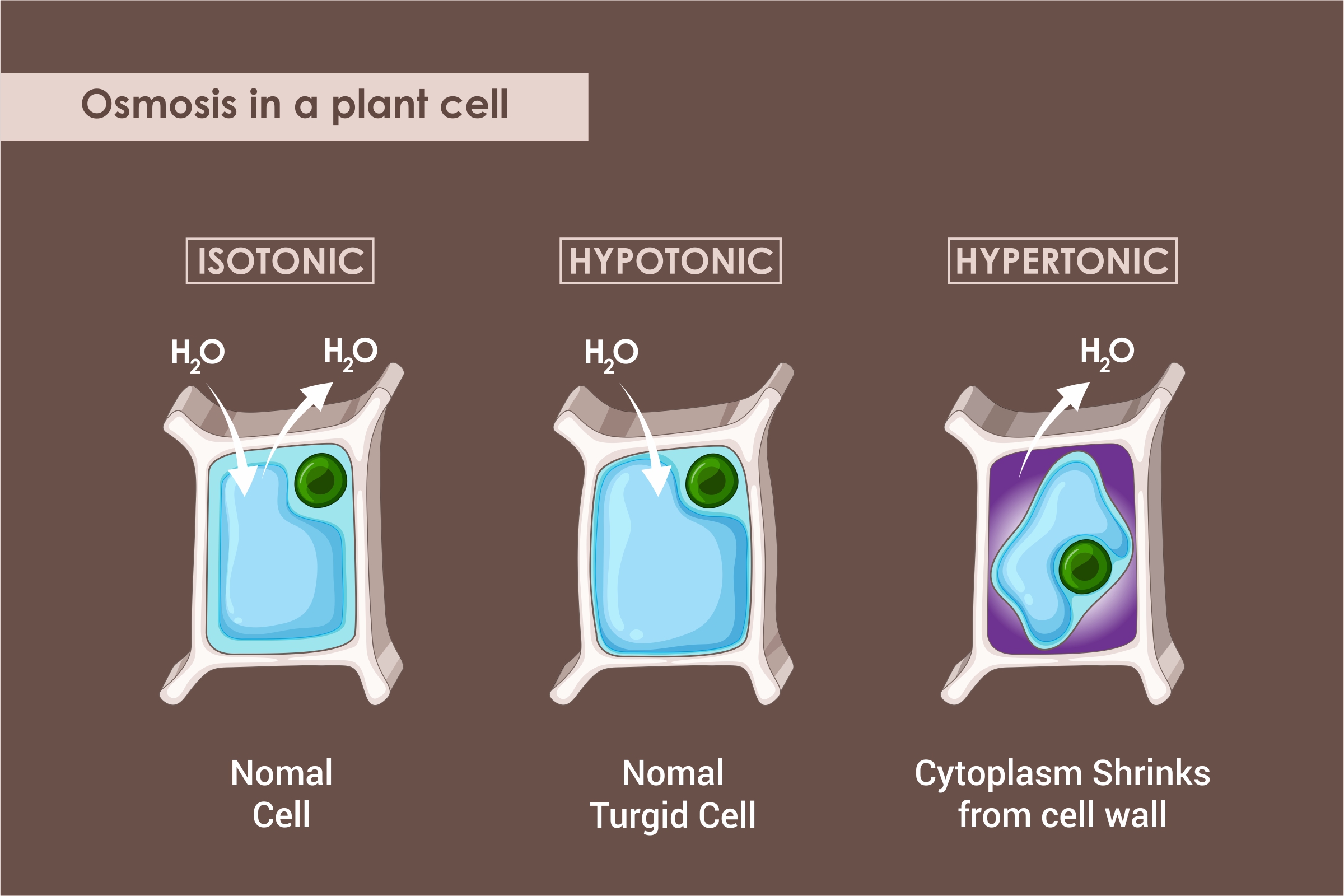
The large permanent vacuole stores several pigments, enzymes, ions, and inorganic and organic substances and plays an excellent role in osmoregulation.
Vacuoles are the essential component of the plant cells, and each plant cell has a large and central vacuole that occupies most of the cell. This central vacuole plays a crucial role in regulating the cell’s water concentration in altering environmental conditions.
In a plant cell, the liquid present inside the large central vacuole endows with the turgor pressure that is an outward pressure caused by the fluid present inside a cell.
Well, let us get a proper understanding of it by the common fact. Well, have you ever noticed that if you do not water a plant continuously for a few days, it wilts?
Undoubtedly, it does. That is all because the water concentration in the soil becomes lower as compared to the water concentration present in the plant. Water moves out of the cytoplasm and central vacuoles into the soil, and since this large central vacuole shrinks, it leaves the plant’s cell wall unsupported.
This loss of support results in the wilted appearance of the plant. And when this central vacuole is filled with water, it endows with a low energy means of the plant cell to expand. Additionally, this fluid can deter herbivory as the waste’s bitter taste discourages its consumption by the animals and insects. The large central vacuole also functions for protein storage in developing the seed cells.