Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
Explain the process of muscle contraction.
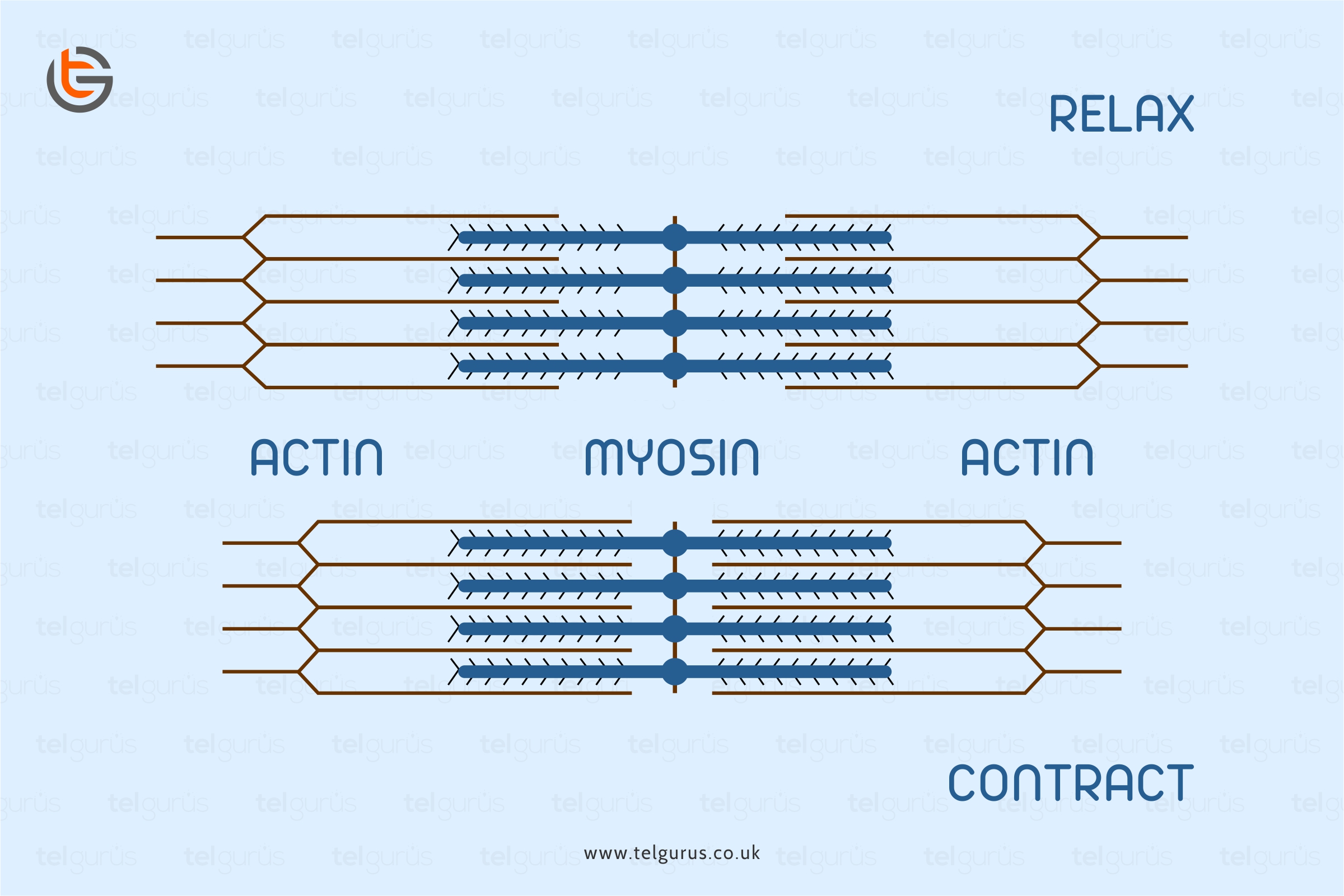
Muscle contraction generally takes place when thick myosin and thin actin filaments slide past each other. Muscle contraction usually takes place when sarcomeres shorten because the thin and thick filaments skid east each other which are known as the muscle contraction sliding filament model.
ATP endows with the energy for filament sliding and cross-bridge formation. The regulatory proteins like tropomyosin and troponin while controlling the cross-bridge formation.
Let us understand the whole concept of the muscle contraction process by getting acquainted with the steps of the whole process.
The muscular contraction process takes place over several steps including
- Depolarisation and calcium ion release
- Actin and myosin cross-bridge formation
- The sliding mechanism of myosin and actin filaments
- Sarcomere shortening
Step 1
Depolarisation and calcium ion release
An action potential from a neuron activates the acetylcholine released into the motor end plate. The released acetylcholine begins the depolarization within the sarcolemma that is spread using the fiber through T tubules.
The depolarization leads to the sarcoplasmic reticulum releasing the calcium ion stores and these calcium ions then play a pivotal role in initiating the muscular contractions.
Step 2
Actin and myosin cross-bridge formation
At this stage, the binding sites for myosin heads on actin are covered by the blocking complex namely tropomyosin and troponin. The calcium ions then bind to the troponin and reconfigure the complex while exposing the binding sites for myosin heads. These myosin heads then generate a cross-bridge with the actin filaments.
Step 3
Sliding Mechanism of Myosin and Actin
The ATP binds to the myosin head while breaking the cross-bridge between the myosin and actin. The ATP hydrolysis then causes the myosin heads to modify the position and swivel while moving them towards the following actin-binding site.
The myosin heads then bind to the new sites and further return to the original conformation. Thus, this orientation drags the actin beside the myosin in a sliding mechanism. Consequently, myosin heads move towards the actin filaments analogously to the manner in when an oar propels the rowboat.
Step 4
Sarcomere Shortening
The myosin heads’ repeated reorientation drags the actin filaments besides the myosin length. Since actin filaments are anchored to the Z lines, the actin dragging pulls the Z lines closer together while shortening the sarcomere.
Since the individual sarcomere becomes shorter in length makes the muscle fibers as a whole contract.
Summarizing the Muscle contractions
Motor neuron’s action potential activates the Calcium ions release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The ions then bind on actin while causing the tropomyosin to move whilst exposing the binding sites for myosin heads.
The myosin heads and actin filaments form a cross-bridge which is broken by ATP and the hydrolysis of ATP leads to the myosin heads to modify the orientation and swivel. The swiveled myosin heads then bind to the actin filaments prior to returning to the original conformation.
The myosin head repositioning moves the actin filaments towards the sarcomere’s center and the actin sliding along with the myosin shortens the sarcomere while causing the muscle contraction.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?