Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
Describe the differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Understanding the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis is imperative. Let us start with the definitions of each.
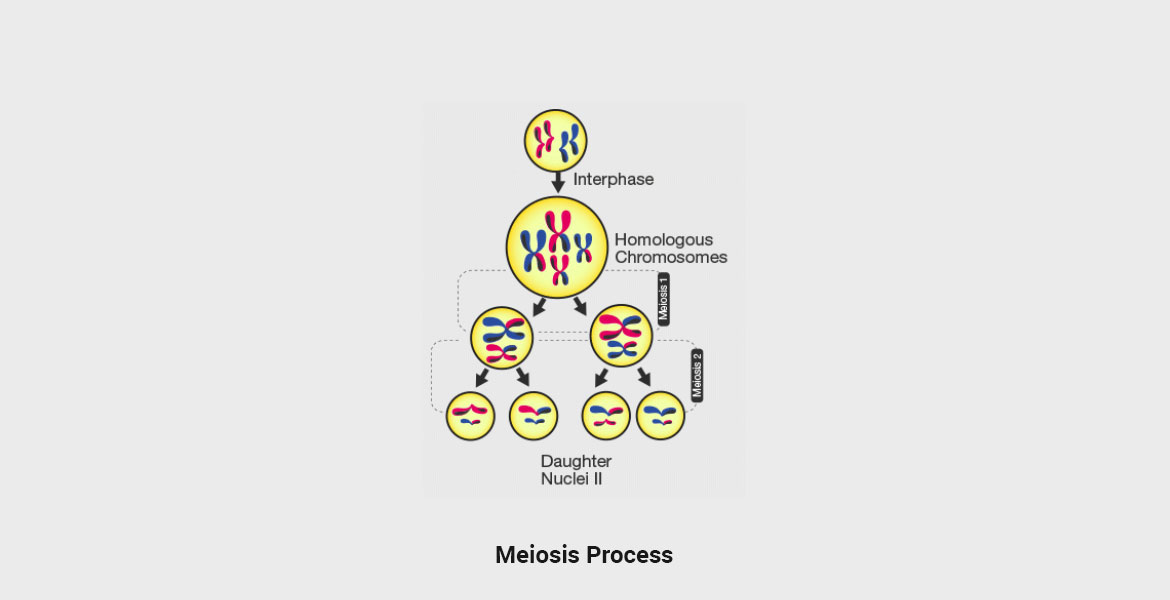
Meiosis
Meiosis refers to a cell division type, which results in the four daughter cells formation, each one with half the chromosomes like the parent cell.
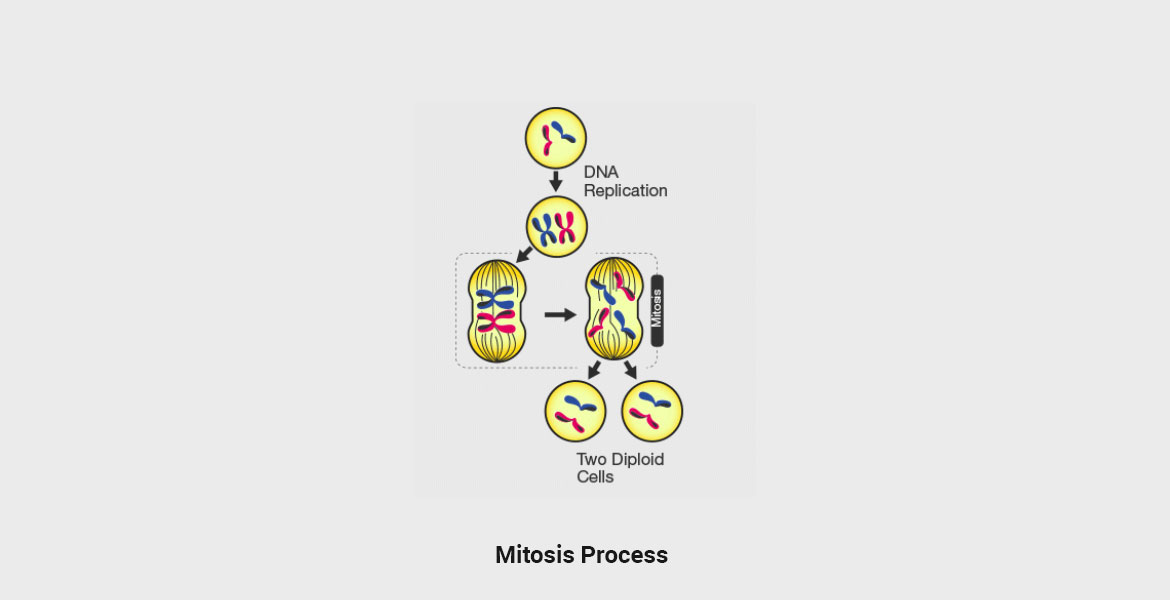
Mitosis is a cell duplication process during which a cell gives rise to two genetically indistinguishable daughter cells. The term mitosis is generally used to describe the distribution and duplication of chromosomes.
Mitosis
Mitosis refers to the cell division type, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells with a similar number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Meiosis is a specialized cell division type that diminishes the number of chromosomes by half, creating the four haploid cells where each one is genetically distinct from the parent cells that give rise to them.
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
| Comparison Parameters | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Cell it produces | It creates somatic or body cells | It creates germ or sex cells |
| Where it occurs | It occurs in all organisms except viruses | It occurs in plants, animals, and fungi |
| Reproduction Mode | Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| Discovered by | It was discovered by Walther Flemming | It was discovered by Oscar Hertwig |
| Function | Its function is to general growth and repair and cell reproduction | Its function is genetic different through sexual reproduction |
| Number of chromosomes | It produces diploid cells that are 46 chromosomes | It produces haploid cells including 23 chromosomes |
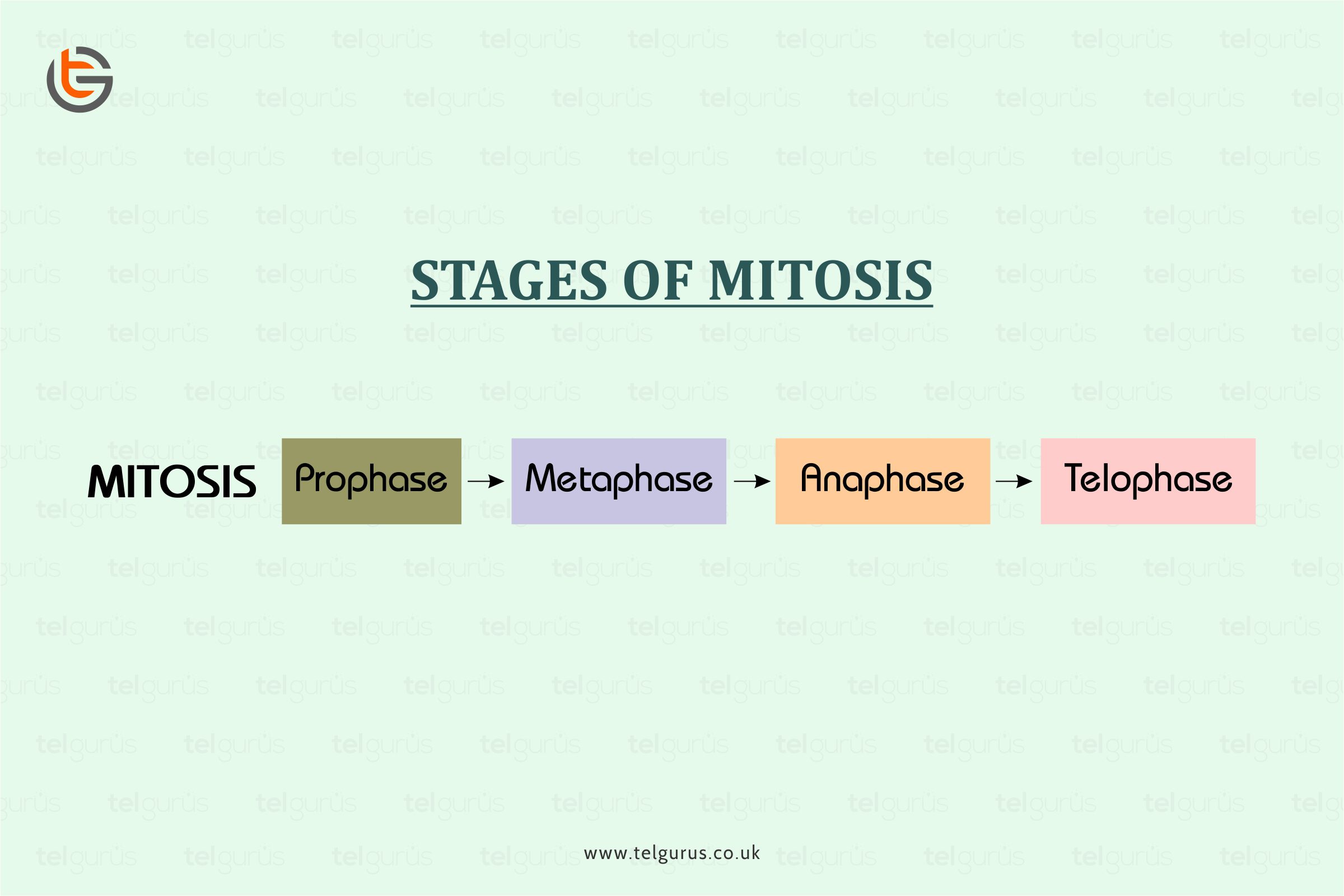
| Stages | It consists of one stage | It consists of two stages |
| Interphase | Here each chromosome replicates | Here, chromosomes are not visible but the DBA has been replicated |
| Prophase Length | Its Prophase length is short | Its Prophase I length is longer |
| Cell Divisions Number | One cell division including 4 stages in total | Two cell divisions including 8 stages in total |
| Crossing over/ Recombination | No crossing over/ recombination in prophase | Crossing over/ Recombination of chromosomes during the prophase I |
| Anaphase | During the anaphase, the sister chromatids move to the cell’s opposite ends. | During anaphase I, the sister chromatids move collectively to the same cell pole whereas, during anaphase II, the sister chromatids are separated to the cell’s opposite ends. |
| Metaphase | During metaphase, individual chromosomes line up on the equator of the cell | During Metaphase I, the chromosome pairs line up on the equator of the cell. |
| Cytokinesis | It occurs in the Telophase | It occurs in the Telophase I and Telophase II |
| Ploidy | It creates the diploid daughter cells | It creates the haploid daughter cells |
| Number of cells created | Two daughter cells are created as a result | Four daughter cells are created as an outcome |
| Genetics | Here, daughter cells are genetically identical | Here, daughter cells are genetically dissimilar |
Bottom Line!
Mitosis is basically a continuous cell division process that occurs in all living cells. In contrast, meiosis is a nuclear cell division, resulting in the daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original cells. Both have several differences that we have compiled above. Hope it gave you a clear idea about both the processes!
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?