Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
How do I find the maxima and minima of a function?
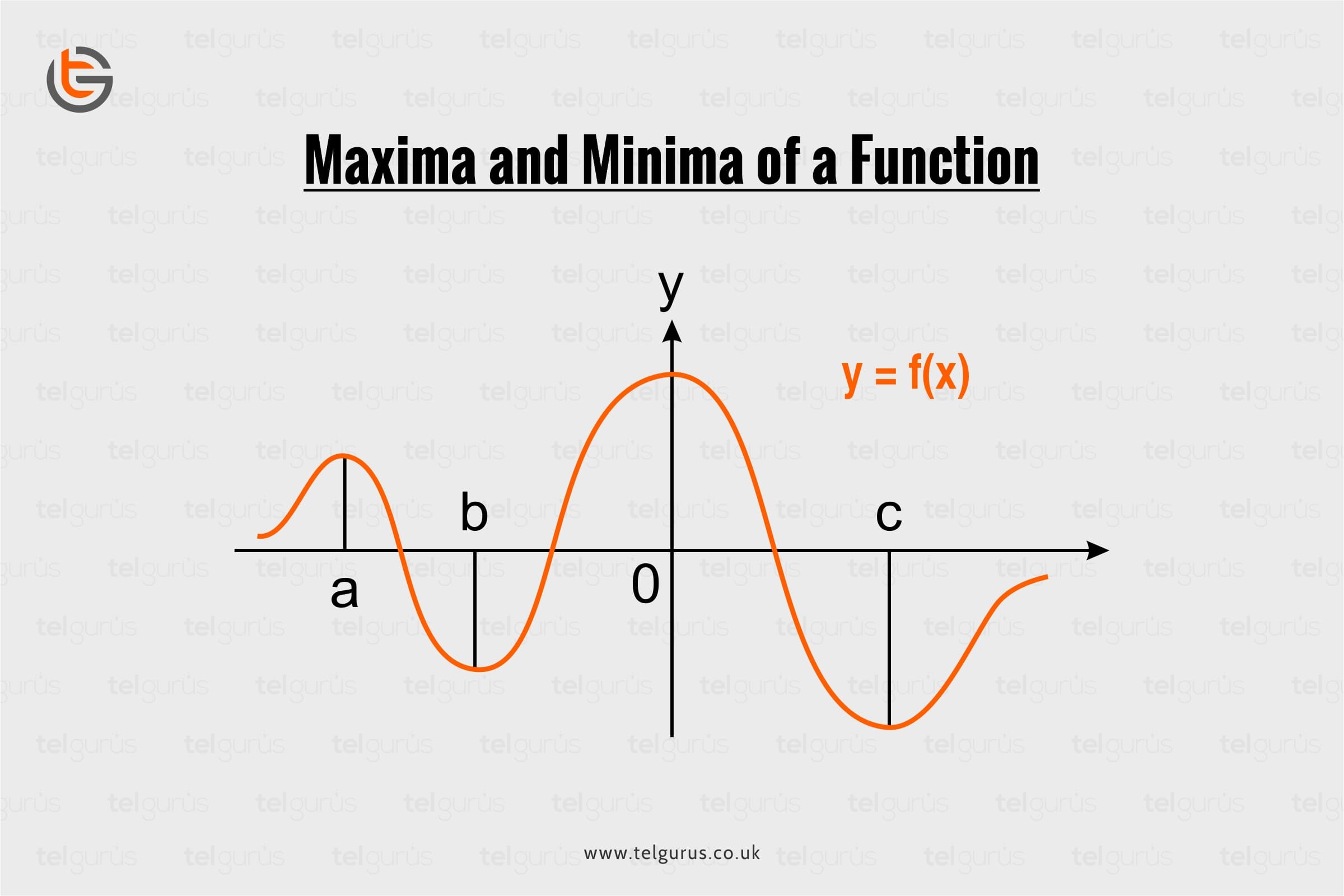
Just like their literal meaning, maxima and minima in mathematics mean finding the maximum and the minimum values of a function within a given domain.
Let’s check a few practical applications of the importance of maxima and minima function.
- To an engineer, these maximum and minimum values of a function helps in determining real life values of a function and help them analyze the practical scenarios and implementation part.
- To an economist, the maximum and minimum values of the total profit function helps to decide the salaries and other expenses of the company so as to keep the budget in control and avoid loss.
- To a doctor the maximum and minimum values of the function help determine the right prescription for the patient.
For example: Values for glucose/sugar levels in the bloodstream are used to determine the dosage the doctor needs to prescribe to different patients to bring their blood glucose levels to normal.
Maxima and minima are respectively the highest and lowest point on the curve.
Let’s discuss how to find the maxima and minima of a function.
Methods to find maxima and minima of a function
Maxima and minima of a function can be calculated by using the first – order derivative test and second – order derivative test.
These are the quickest ways to find the maxima and minima.
First order derivative test for Maxima and Minima
The first derivative of any function gives you the slope of the function.
Near a maximum point, the slope of the curve increases as we go towards the maximum point then becomes zero at the maximum point and then decreases as we move away from the maximum point.
Similarly, is in the case of minima.
Let say we have a function f which is continuous at the critical point, defined in an open interval and f’ ( c ) = 0.
Then we check the value of f’( x ) at the point left to the curve and right to the curve and check the nature of f’( x ), then we can say that the given point will be:
# Local maxima : If f’ ( x ) changes sign from positive to negative as x increases via point c, then f ( c ) gives the maximum value of the function in that range.
# Local minima : If f’ ( x ) changes sign from negative to positive as x increases via point c , then f ( c ) gives the minimum value of the function in that range .
# Point of inflection : If the sign of f’( x ) doesn`t change as x increases via c, and point c is neither the maxima nor the minima of the function , the point c is called the point of inflection.
Second order derivative Test for Maxima and Minima
In the second order derivative test for maxima and minima, we find the first order derivative of the function and if it gives the value of the slope equal to zero at the critical point x = c [( f’ ( c ) = 0 ] , then we find the second derivative of the function. If the second order derivative of the function exists within the given range, then the given point will be:
# Local maxima: If f’’ ( c ) ˂ 0
# Local minima: If f’’ ( c ) ˃ 0
# Test fails: If f’’ ( c ) = 0
So, by these two methods we can find the maxima and minima of a function.
Read More – Mathematics Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development

Unleash the Power of visualization to break tough concepts
Wanna be the next Maths wizard? Discover the new way of learning concepts with real-life Visualization techniques and instant doubt resolutions.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?