Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is the difference between alpha and gamma radiation?
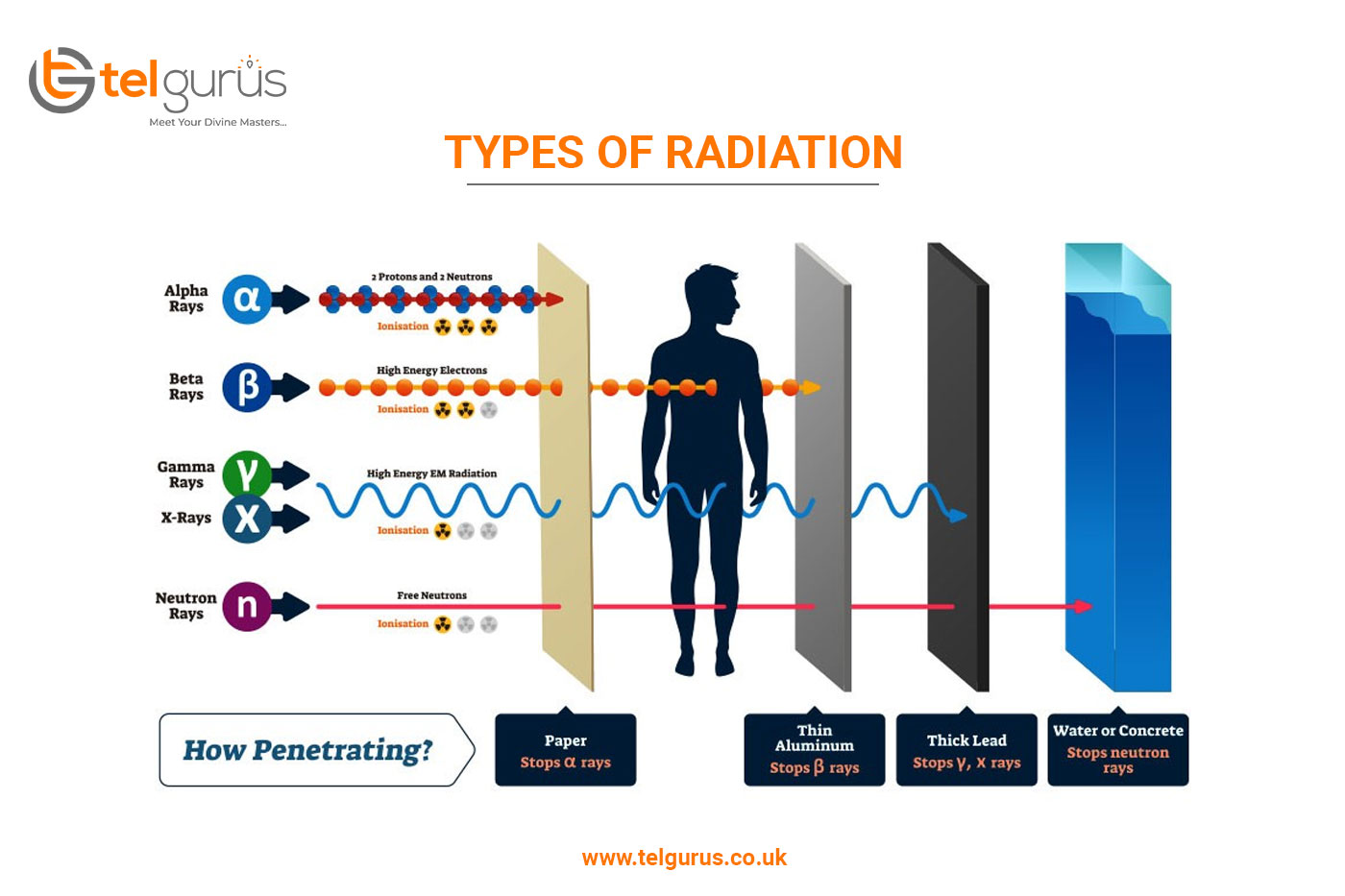
Radioactivity is an act of emitting radiation spontaneously. It is an unstable atomic nucleus to achieve a stable configuration by giving up some of its energy. During radioactivity, three primary types of radiation are emitted by radioactive particles including alpha, beta, and gamma.
The three major radiation types emitted by radioactive particles include
- Alpha
- Beta
- Gama
These radiations are released from the atom’s nucleus and are emitted by the atom because of an unstable atom trying to gain stability.
And even their behaviors differ from one another. So, let us take a closer look at each type.
Alpha Particles
Alpha particles are the largest particles with the least penetrative power. It carries a positive charge and comprises two protons and two neutrons bound together. An alpha particle later got recognized as helium 4 nucleus.
These particles have the greatest mass among the other types of radioactive emissions. An alpha particle’s mass is around 8000 times more than the beta particle’s mass. This large size of an alpha particle reduces its penetrative power.
Properties of alpha particles
- Alpha particles are heavy, positive, and slow in movement.
- The alpha particle’s travel speed is five to seven percent of the speed of light.
- In cancer treatment, radiotherapy uses alpha particles to kill cancer cells.
Beta Particles
Beta particles are high-energy positrons or electrons carrying a negative charge. These are considerably smaller in size and have higher penetrative power.
Properties of Beta particles
- Beta particles are used as a trace for medical imaging
- Beta particles carry a positive charge namely a positron or a negative charge namely an electron
- Due to their small mass, beta particles travel at the speed of light
- Beta particles have therapeutic uses in eye cancer and bone treatment.
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are not particles with a mass. These are a kind of electromagnetic radiation which are considerably higher in energy as compared to X-rays. Being a form of energy, gamma rays have no mass and size. But these are far more harmful to humans as compared to the X-rays. However, the charge of gamma rays is neutral.
Properties of Gamma particles
- Gamma particles have no mass
- Gamma particles have no electrical charge
- It can also travel at the speed of light
- Gamma rays are used for sterilizing medical instruments and oncology.
Comparison chart
| Basis for comparison | Alpha | Beta | Gamma |
| Representation | α | β | γ |
| Charge | It is positively charged | It is positively or negatively charged | It has no charge |
| Basic | It is similar to helium nucleus because of protons presence | It is a positron or an electron | It’s a photon that carries electromagnetic energy. |
| Propagating speed | It is very less than the velocity of light | It is a little less than the velocity of light | It is equal to the velocity of light |
| Size | It’s quite large | It is comparatively small | It is extremely minute because it is massless. |
| Mass | 6.65*10-27 Kg | 9.10*10-31 Kg | 0 |
| Application | In an unsealed source radiotherapy | In monitoring material thickness | In nuclear industry |
Read More – Physics Questions

Accelerate your learning in the right Dimension!
Instant doubt resolution and practical exposure to concepts, makes learning Physics easy and fun.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?