Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is active transport in Biology?
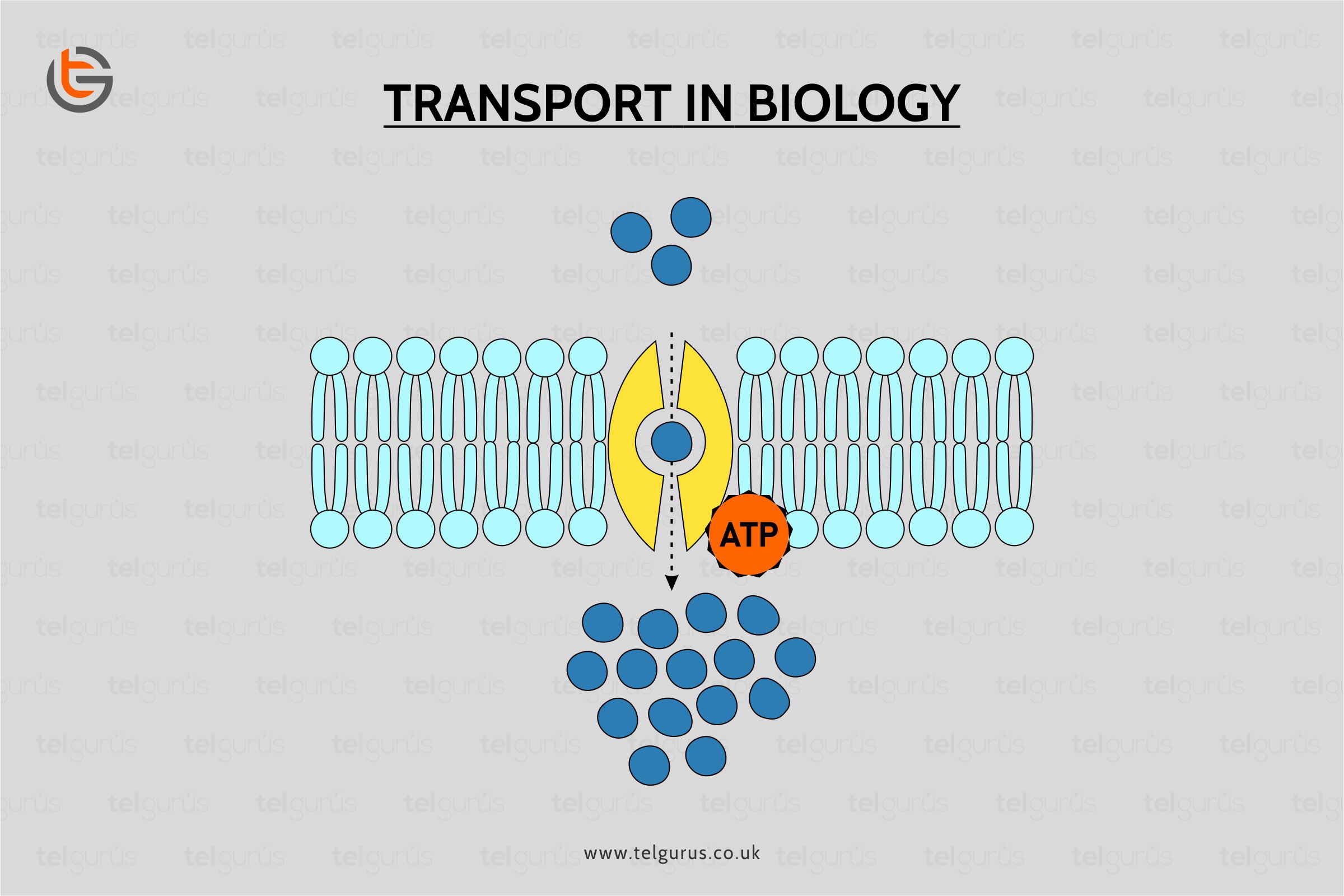
Active transport is a process that involves the molecule’s movement from a lower concentration’s region to a higher concentration’s region against an obstacle or a gradient with external energy’s use.
During the active transport process, a protein pump uses the stored energy in ATP’s form to move the molecules. Transportation is a natural, essential, and physiological process in all the higher organisms like animals, plants, and humans.
Examples of active transport include:
- Glucose uptake in the human body’s intestine
- Minerals or ions uptake into plant’s root hair cells
- Bacteria’s Phagocytosis by Macrophages
- Amino acids transportation across an intestinal lining in the human gut
- Protein’s secretion like peptide hormones, enzymes, and antibodies of different cells.
- WBCs function by protecting the body by attacking diseases causing foreign invaders and microbes.
Types of Active Transport!
There are two types of active transport.
- Primary active Support
In the Primary active transport process, the energy is utilized by ATP’s breakdown to transport the molecules across the membrane in opposition to a concentration gradient.
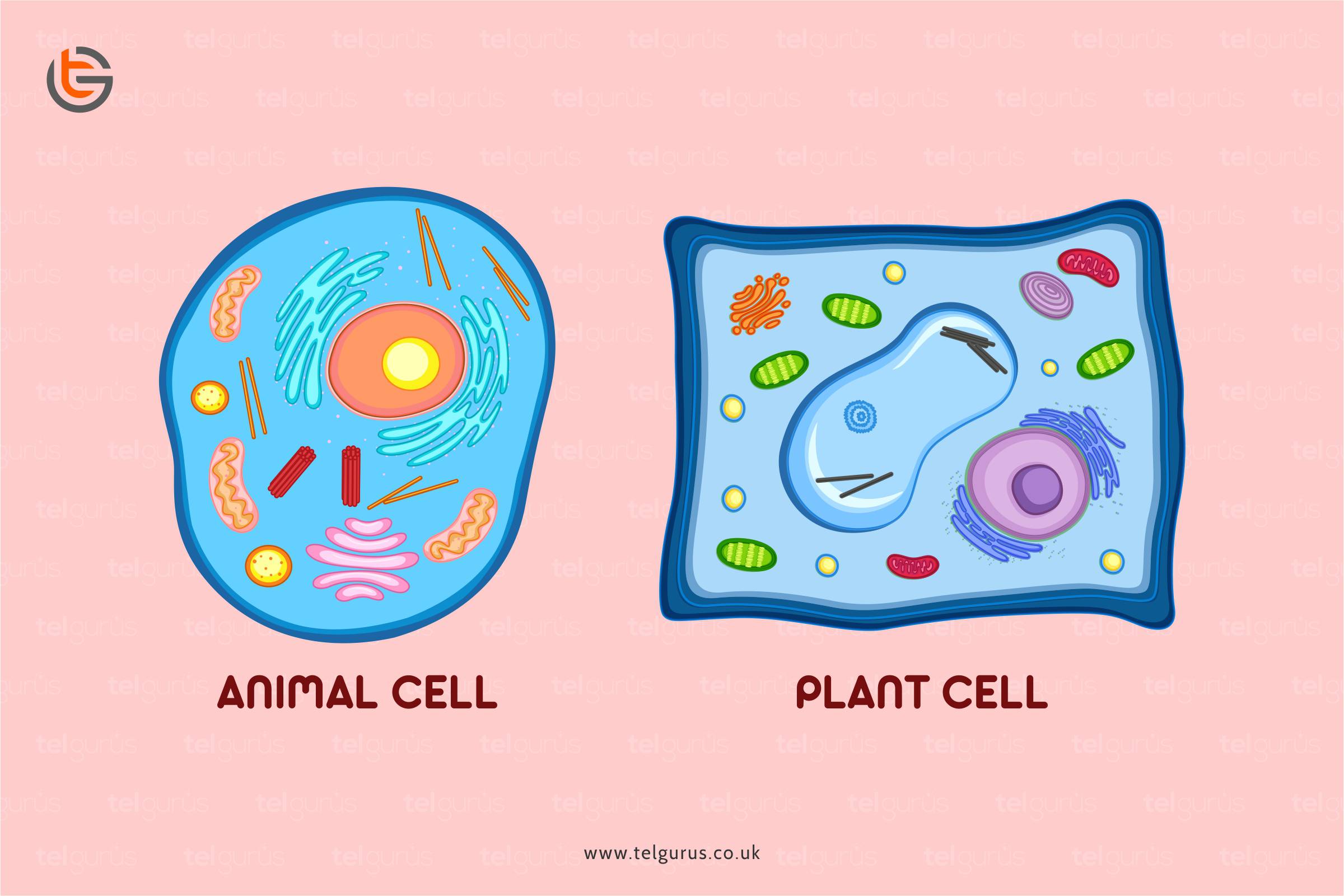
Consequently, ATP power pump’s groups comprise one or more binding sites for ATP molecules present on the membrane’s cytosolic face. Therefore, it can be said that the primary active transport utilizes external energy like ATP. Sodium potassium pump in an animal cell is an example of primary active transport.
- Secondary Active Transport
Secondary active transport takes place across a biological membrane where the transporter protein couples electrochemical ion’s movement. The secondary active transport utilizes electrochemical energy.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
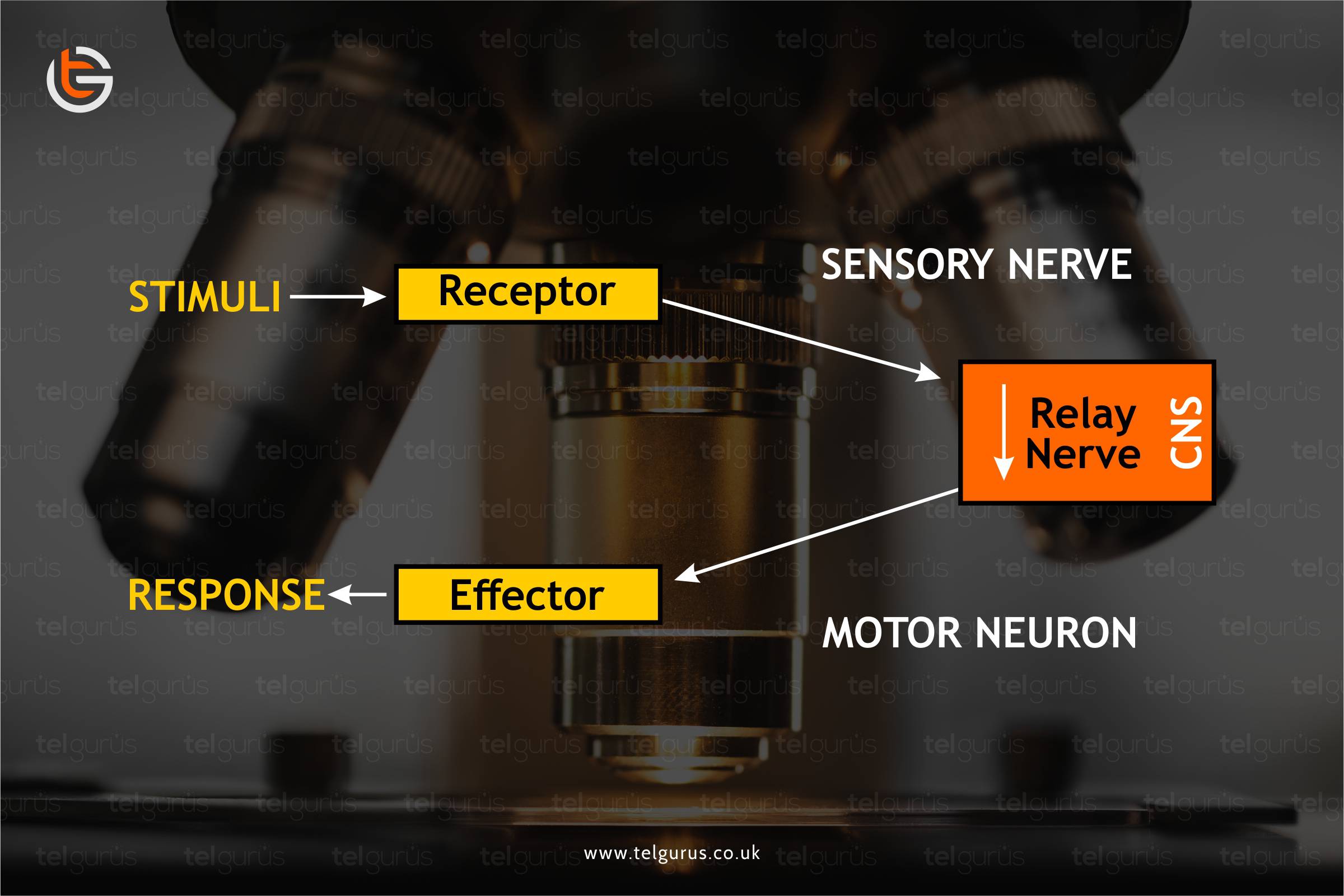
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?