Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is the role of the Nucleus?
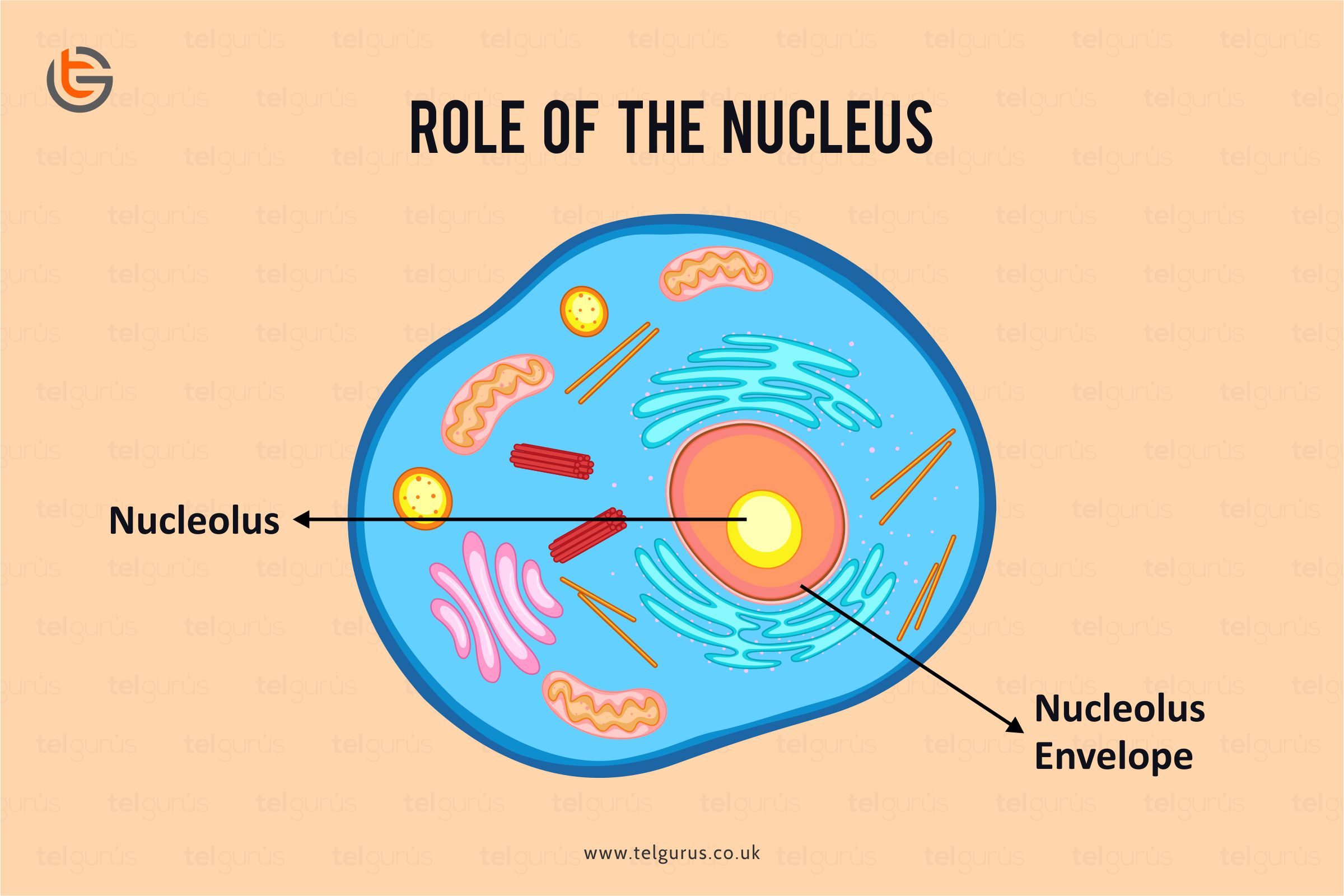
The Nucleus is an essential organelle of a cell that acts as a blueprint for how the cells present in the body function. It is responsible for regulating all forms of cellular activities.
Let us get acquainted with the essential information concerning the Nucleus, starting with its definition.
What is Nucleus?
The Nucleus is the most integral component of a cell. It is derived from a Latin word that means “Kernel of a nut.”
It is defined as a double membrane eukaryotic cell organelle, which contains genetic material.
Structure of a Nucleus
The Nucleus is the most evident organelle in a cell that is entirely bound by the membranes. It is the largest organelle that is present in the human body occupying almost 25 percent of the cell volume.
The structure of a nucleus is divided into four main parts. This includes:
- The Nuclear envelope
The Nucleus is bound by a double membrane layer which forms the envelope or the capsule. This envelope’s two layers stay separated from each other by a space often known as the perinuclear space. It generally separates the nucleus’ inner contents from the rest of the cell.
The nuclear envelope’s outer layer is rough due to the ribosome’s presence on its surface. Also, the nuclear membrane has tiny gaps known as the pores that allow the substances’ selective package between the cytoplasm and Nucleus.
Key points of Nuclear envelope
- It is made up of a membrane phospholipid bilayer having outer and inner membranes.
- It helps in maintaining the shape of the Nucleus
- It encloses the nucleoplasm
- It is connected to the Endoplasmic Reticulum
- The Chromatin
The DNA is prearranged in the Nucleus to form chromatin. The chromatin contains the proteins and condenses further to generate the chromosomes. A human cell has a total of 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Key Points of Chromatin
- The chromatin contains proteins
- The chromatin condenses to form the chromosomes.
- The nucleolus
It’s a well-defined spherical structure that is present within the Nucleus. It is basically the site for the ribosomes’ synthesis and assembly. Here the ribosomes act as protein synthesis sites within the cell.
Key Points of Nucleolus
- It appears as a darker part of the Nucleus when analyzed with a microscope
- The Ribosome synthesis takes place here
- The nucleoplasm
The nucleoplasm is also known as karyoplasm or nuclear sap. It is a granular, semi-solid substance that comprises several proteins.
The protein fibers generate a crisscross matrix within the Nucleus that helps maintain the structure and the shape of the Nucleus. It is basically the main site for the enzyme activity within the Nucleus.
However, the nucleoplasm appearance may vary during the various phases of a cell cycle.
Along with the proteins, the nucleoplasm also comprises other substances, including RNA, DNA and nucleus.
Key Points of Nucleoplasm
- Chromatin is the DNA wrapped around proteins
- It’s a gel-like material that chromatin is stored in
Functions of the Nucleus
The Nucleus performs several essential functions in a cell. The three primary functions of the Nucleus include
- It comprises the cell’s genetic information in the form of DNA or chromosomes and, therefore, controls cell multiplication and growth.
- It is also regarded as the site of DNA replication where the formation of an identical copy of DNA occurs.
- It is responsible for regulating metabolism by synthesizing several enzymes.
- It is the site for RNA synthesis that acts as a template for the synthesis of several proteins present in the cell.
Bottom Line!
A nucleus is a double membrane organelle consisting of the genetic material and other instructions needed for the cellular process. The Nucleus has two primary functions, including
- A nucleus is responsible for the hereditary material of a cell.
- It is also responsible for coordinating several essential activities like cell division, protein synthesis, cell growth, and a host of other vital functions.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?