Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What causes or reduces resistance in a material?
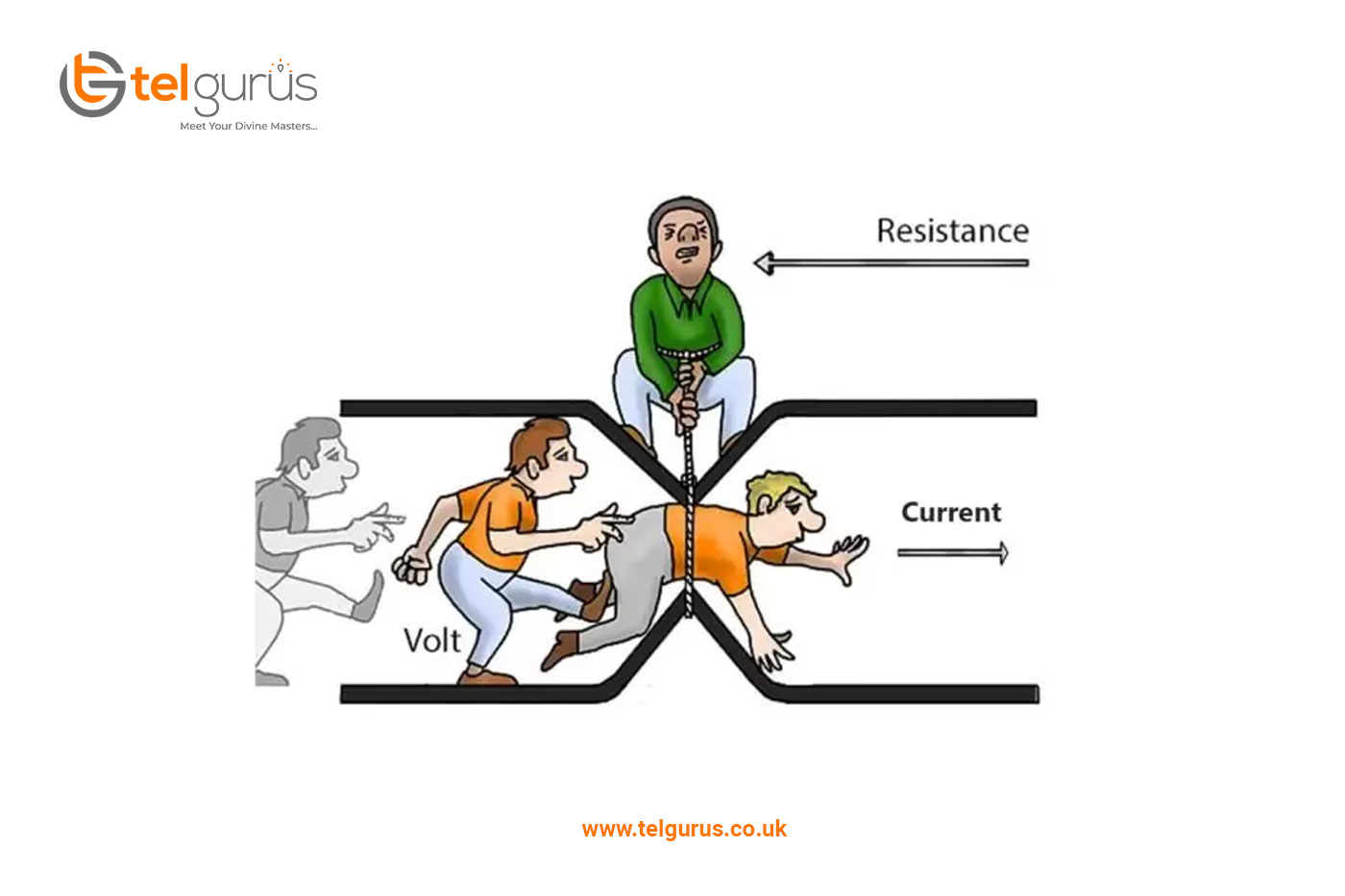
Resistance is referred to as an obstacle to the electron’s flow in a material whenever the potential difference is applied across the conductor, which aids in the movement of the electrons. In contrast, resistance opposes the movement of the electron.
Whenever the voltage is applied across a substance, an electrical current is produced, and the voltage applied across the substance is directly proportional to the current. This is represented by
V∝I
The proportionality constant is known as the resistivity of materials resistance.
V=RI
Therefore, resistance is defined as the voltage ratio applied through the substance to the current.
Well, let us take an example to understand resistance,
Think about the break time in your school, when all the students are outside the classroom, stay in the field relaxing, playing and some are sitting in groups. As the school bell rings, all get up and starts moving towards their respective classes. Well, where you are in the open field, ample children can walk together to move towards their destinations that are their respective classes.
But when you come closer to the classroom, there is just a door allowing one or two children to move at a time as the door is narrower as compared to the corridor or, say, field. The corridor or the field has a higher resistance as compared to the classroom door. A similar concept is the movement of electrons.
So how does this concept apply to electrical resistance?
Resistance is defined as an electrical circuit that opposes the passage of electrons. So, got it relatable, like the narrowed door limited the passage of students, the resistance opposes the passage of electrons.
Where there is current through any material that has resistance, heat is generated by free electrons collisions and atoms. And consequently, a wire that has small resistance becomes warm where there is enough current to pass through it.
What is the unit of resistance?
The unit of resistance is the ohm, represented by the Greek letter omega.
Therefore, the unit of resistance is Ω.
Resistance of different materials
- Conductors: Conductors are materials that offer far less resistance to electrons flow. For instance, silver is a good electricity conductor, but because of its higher costs, it is not commonly used in electrical systems. Aluminum is also a good conductor that is widely used.
- Semiconductor: Semiconductors are materials that offer moderate resistance value. That means not very high and not very low. Germanium and silicon are the two most commonly used semiconductors.
- Insulators: Insulators are materials that offer very high resistance to the electron’s flow. But there are very bad electricity conductors and are mainly used to prevent current leakage. Porcelain, mica, dry wood are some excellent examples of insulators.
What causes or reduces resistance?
Electrical resistance has to do with the material the electrons or electricity are passing through. The more free electrons that can be tattered from the atoms, the less the resistance. The cause and reduction of resistance depend on several factors. Several factors affect resistance which in turn is responsible for the cause and reduction.
Resistance decreases with an increase in temperature. There are four factors on which the cause and reduction of resistance depend.
- Length
- The type of material
- It’s the cross-sectional area
- The nature of the material.
The resistance depends on the length, nature, material, and cross-sectional area of a wire.
Do you know?
- Thick wires have less resistance as compared to thin wires.
- Longer wires adhere to more resistance than shorter ones.
- Copper wires have less resistance as compared to steel wires of similar size.
Read More – Physics Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development

Accelerate your learning in the right Dimension!
Instant doubt resolution and practical exposure to concepts, makes learning Physics easy and fun.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?