Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
How are nerve cells adapted to their function?
Understanding the answer to this requires a comprehensive understanding of the nerve cell’s functioning.
Neurons require to be rapidly able to transmit the electrical impulses along with their lengths. This also requires the signal exchange with the neighboring neurons across the gaps popularly recognized as “SYNAPSES,” which separates them.
So, in order to attain these functions, the nerve cells include various adaptations.
Each neuron requires three different parts. This includes:
- Cyton
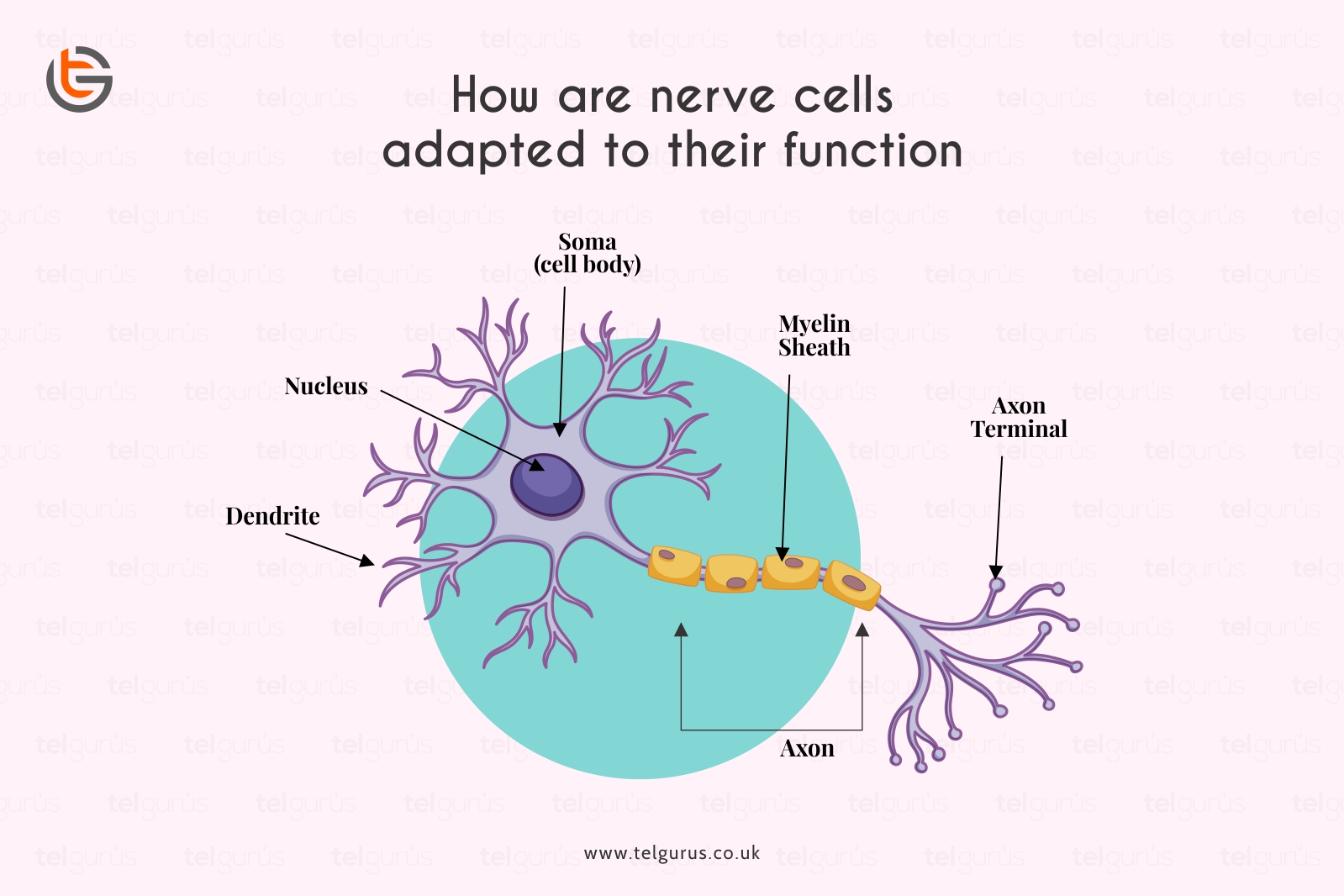
Cyton is the central body of the neuron, which contains the nucleus and cytoplasm. This cytoplasm shows the Nissl’s granules characteristics and receives the electrical impulses from the other neurons through dendrites.
- Dendrites
Dendrites refer to the neurons’ thin long projections which receive the signal from others. Its structure is similar to the tree-like branch system while forming the points becoming stimulated by the other neurons. It also conducts the impulses to the cell body.
- Axon
Axon, popularly known as the nerve fiber, refers to the nerve cell’s portion. It carries the nerve impulses away from the body of the cells. And the ending of the axon connects with other neurons, gland cells, or muscles.
The Nerve Cells
The nerve cells allow communication with the different parts of the body. The dendrites have a higher surface area that enables contact with other neurons, and the myelin sheath surrounding the axon acts as an insulator.
Now that the basic statements and terms are clear, let us understand the process.
Understanding the nerve cell functioning
The long thin part of the neuron known as the axon along which the impulses pass is generally covered in the fatty myelin sheath that acts as an electrical insulator.
This enhances the transmission speed by forcing the impulses to jump among gaps within the sheath, popularly referred to as Ranvier.
Nerve cells also include a lot of mitochondria that provide the desired energy to synthesize the neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, which passes the message across the synapses.
Additionally, the dendrites and numerous fine extensions to the cell body at one cell’s end provide a higher surface area which permits the nerve cell to generate synapses with several others.
However, identical branching at the cell’s other end and synaptic knobs at the branch end store the neurotransmitter, which is ready to diffuse across the synapse as an impulse arrives.

Get your doubts resolved ON THE SPOT!
Make learning interesting and fun when the doubts are resolved instantly with the comfort of your home only at TEL Gurus.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?