Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
WHAT DOES POLARITY MEAN IN BIOLOGY?
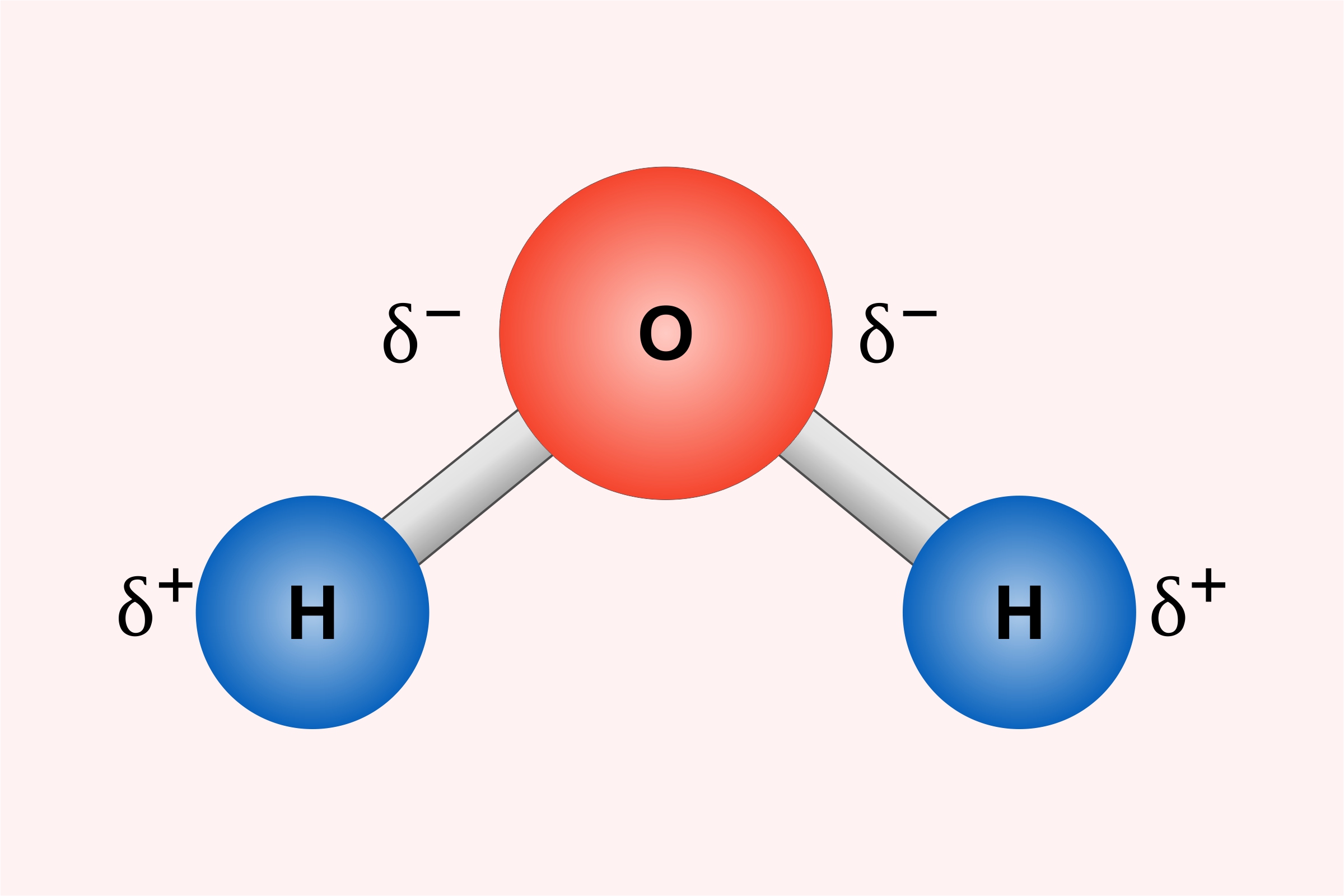
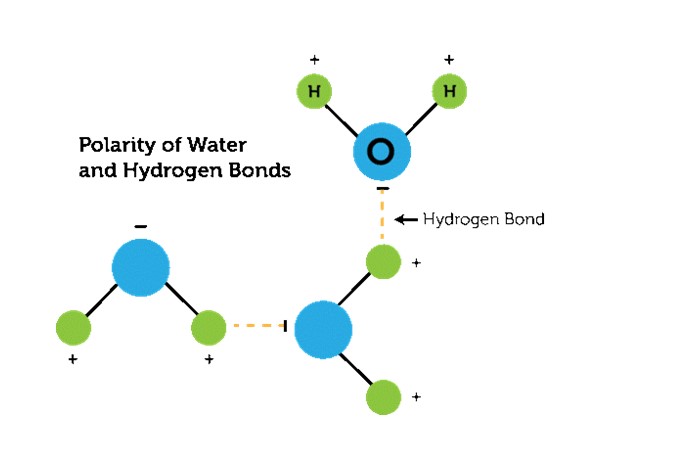
We often study Polarity, and you must have a good idea about what exactly it is. The atoms and molecules which have both positive and negative charges are Polar. The electrons are shared unequally and the atom having more electronegative force attracts the other atom towards it.
For example, H2O or water is made up of 2 Hydrogen and 1 Oxygen atom. Being more electronegative, the O attracts the H atom and forms a covalent bond. The oxygen atom has six electrons in the valance shell which are more than that of Hydrogen. Due to this, O attracts H strongly and reacts to form water molecules.
From this, O atoms gain slightly negative and slightly positive electrons. These attractions between the molecules are called Intermolecular Forces.
- The atoms are covalently bonded, and the charges are distributed unevenly. This results in the attraction of the least negative atom to the highly electronegative atom. In this way, a new molecular structure is formed.
- Greater the ionic difference, greater will be the polarity of a species.
- In Biology, polar describes how the water molecules interact with other atoms and particles of an organism.
- The atom which attracts the atom due to its high electronegative power is known as the ‘Polar atom’.
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?