Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is the difference between a receptor and an effector in the nervous system?
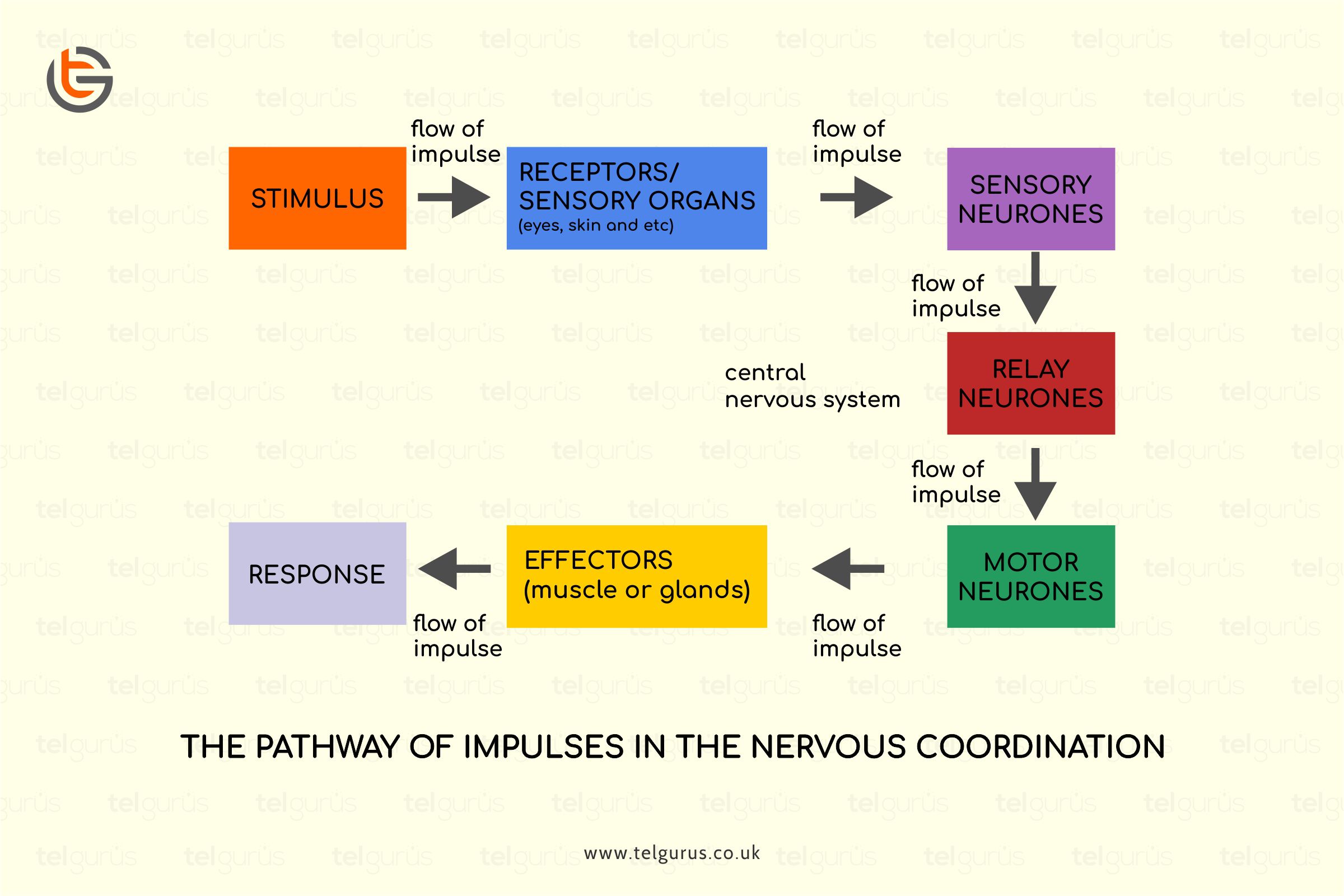
The receptors are sensitive to the changes occurring in internal or external environments, whereas the effectors are the glands or muscles that produce action in response to the stimulus.
Both the terms have several similarities and key differences. Let us get acquainted with each one of them.
What is a receptor?
A receptor identifies, detects the stimuli, and converts them into an Impulse.
The receptor generally receives the electric signals. An example of a receptor includes the light receptors in the eye.
Receptors are the cells or a group of specialized cells that can detect some change in the stimulus or environment and generate electrical pulses in the response.
The sense organs are composed of the receptor group that responds to a particular stimulus.
Sensory nerves carry the impulse produced from the stimulus to the central nervous system to process; after processing and interpreting the signals, the central nervous system sends the information to the effectors to generate a response.
What is an effector?
Effectors are the organs that manifest the central nervous systems’ instructions according to the external stimulus. The example of an effector includes a muscle.
Effectors are the body parts like glands and muscles that generate a response to a detected stimulus. These are present in any of the body parts, and motor neurons carry the impulses to effectors.
Once the effectors obtain the impulses, they respond immediately to convert them into actions.
For instance, a muscle contracting to move an arm or a gland liberating a hormone into the blood.
Similarities between receptor and effector
- Both the effectors and receptors respond to stimuli
- They convert or generate nerve impulses
- Information flows from receptors to effectors
- They work with the central nervous system
- They are connected to neurons
Understanding the differences between a receptor and an effector in the nervous system
| Parameter | Receptor | Effector |
| Main action | Receptors respond to the stimulus | These are the organs that produce a response |
| Function | It sends information to the central nervous system | It obeys the commands of the central nervous system |
| Where it is present | It is present in the sense organs only | These are present all over the body |
| Examples include | The light receptors in the eye
OR Ears sound receptors |
Muscles contract to move an arm
OR A gland releases a hormone into the blood. |
| Definition | The receptor detects the stimuli and covers them into an impulse | Effector converts an impulse into action. |
| Detailed Definition | It is a cell or a group of cells that are present in the sense organs that are sensitive to a specific type of stimuli like sound, smell, light, heat, taste, or temperature. | It is a body part that responds to the stimuli as per the instructions sent from the central nervous system. |
| Connected to? | These are connected to the sensory nerves | These are connected to motor nerves. |
| Present in | Sensory organs | All over the body |
| Type of structure | A group of cells of a sensory organ | A gland or muscle |
Bottom Line!
The major difference between the receptor and effector of a nervous system is that a receptor detects the stimuli and converts them to an impulse. In contrast, an effector converts an impulse into action.
Read More – Biology Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development
Visualize the in-depth understanding of the natural world!
Biology would sound more interesting when your curiosity levels are satisfied with better visuals & logical explanations.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?