Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
Describe the differences between the three types of bonding
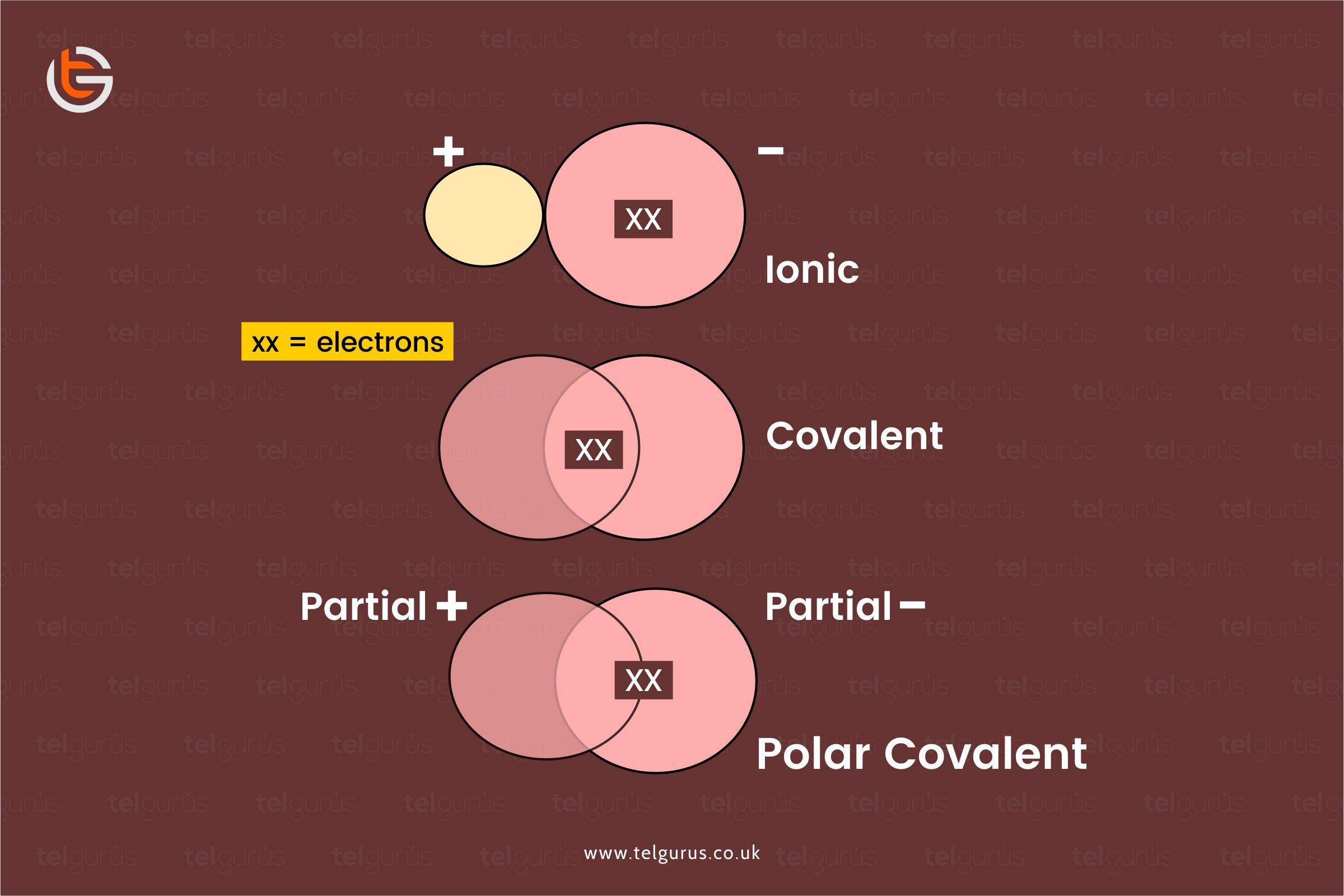
The three types of bondings are namely
- Ionic Bonding
- Covalent bonding
- Metallic Bonding
Let us get acquainted with all the essential information concerning all three types of bondings.
What is ionic bonding?
Ionic bonding is the one that takes place between metals and non-metal atoms.
This type of bonding generally involves the electrons transfer from metal to non-metals developing a negatively charged non-metal ion and a positively charged metal ion.
For instance, Na+ and Cl- making NaCl.
These are more like the blood donations where a metal atom gives its electrons to a non-metal atom.
Since the electrons are negatively charged, that means the metals become more positive while the non-metals become more negative. Just like south and north on a magnet!
What is covalent bonding?
Covalent bonding takes place between the non-metal atoms only. Here instead of the electrons transfer taking place in the ionic bonding, this type of bonding includes the electrons sharing between the non-metal atoms.
For instance, H+ and OH- make H2O.
Covalent bonds are the ones where two atoms share their electrons. The orbitals that electrons sit in overlie between one atom and the next. This satisfies both the atoms and makes them stable.
Some of the two non-metal atoms that cannot even easily move away from each other are more like the blood brothers.
What is metallic bonding?
Metallic bonding is the one that is different from other types of bonding as it occurs between metal atoms only.
Here the metal atoms are arranged in a regular pattern in which the electrons in the outermost shell are delocalized and form solid metallic bonds.
For instance, Metals like iron, zinc, etc.
Here the extra electrons present in the metal atoms are dropped, making the metal a positive ion.
And the extra electrons become an electrons sea that is negative, so the positive metals stick to the negative electrons while forming a large metallic lattice structure.
Understanding the differences between the three types of bonding
| Parameters | Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond | Metallic Bond |
| Occurrence | It occurs during the electrons transfer | It takes place when two electrons share their valence electrons. | It takes place during the attraction of metal atoms/ cations and delocalized electrons |
| Binding Energy | Here the binding energy is higher than the metallic bond. | Here the binding energy is higher than the metallic bond | Here the binding energy is lower than the ionic and covalent bond |
| Bonds | Non Directional bonds | Directional bonds | Non-directional bonds |
| Conductivity | It has Low Conductivity | It has a Very Low Conductivity | It has a higher electrical conductivity/ |
| Molding property | It is unmoldable | It is unmoldable | It is moldable |
| States | It is present in only one state that is the solid state | It is present in all three states including the solids, liquids, and gases | It is present in only one state that is the solid state |
| Ductile property | It is non-ductile | It is non-ductile | It is ductile |
| Melting Point | It has a higher melting point | It has a lower melting point | It has a higher melting point |
| Boiling point | It has a higher boiling point | It has a lower boiling point | It has a higher boiling point |
Bottom Line!
The major differences between all three bonds can be summed up like
- Ionic bonds are formed due to the electron transforming from one atom to another.
- The electron sharing between two atoms forms covalent bonds.
- Metallic bonds are formed between the metal atoms and valence electrons.
Read More – Chemistry Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development

Discover the exact logic behind the reactions!
Get a deeper understanding of every possible interaction between atoms, molecules and elements in an easy and fun-loving way.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?