Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is Pythagoras Theorem?
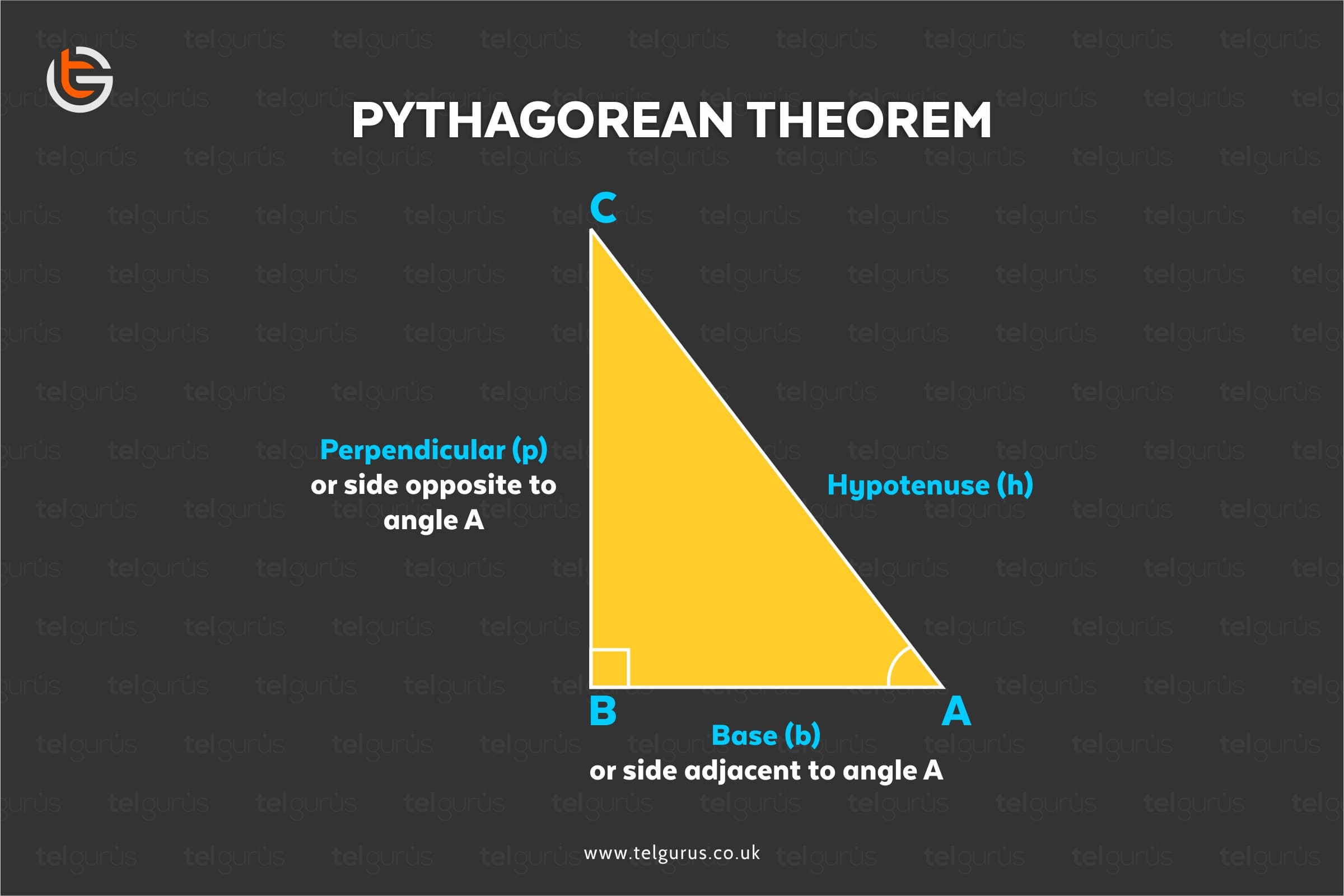
Just like other concepts, Pythagoras theorem has its own relevance in mathematics. It explains the relation between the sides of the right-angled triangle. This theorem was invented by famous Greek mathematician named “Pythagoras”.
This formula states the relationship between base, perpendicular and hypotenuse of a right angled triangle. Let’s discuss the same in detail.
Pythagoras Theorem
According to Pythagoras Theorem, “In a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides which are knows as base and perpendicular”.
Let’s us understand the concept.
As we know that in a right triangle we have three sides Hypotenuse, perpendicular and base. The side that is opposite to the 90 degree angle is called the hypotenuse which is also the longest side.
So, according to Pythagoras theorem:
\displaystyle (\text{ }Hypotenuse~){{~}^{2}}~~~=~~\text{ }{{\left( {\text{ }Base\text{ }} \right)}^{2}}~~\text{ }+\text{ }\left( {\text{ }Perpendicular\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
In the above right triangle ABC right angled at B , side AC is the hypotenuse (the longest side), side BC serves as the base and side AB is the perpendicular.
The base and perpendicular can be used interchangeably.
So, according to Pythagoras Theorem
\displaystyle (\text{ }AC~){{~}^{2}}~~~=~~\text{ }{{\left( {\text{ }BC\text{ }} \right)}^{2}}~~\text{ }+\text{ }\left( {\text{ }AB\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
So, this Pythagorean Theorem builds a relationship between all the three sides of a right angled triangle.
We can use this theorem to find the unknown side of a triangle when two of its sides are given.
Let us take some examples:
Example 1
Question. Find the hypotenuse of a right triangle if the base is 3 cm and perpendicular is 4 cm ?
Solution: According to Pythagoras theorem
(\text{ }Hypotenuse~){{~}^{2}}~~~=~~\text{ }{{\left( {\text{ }Base\text{ }} \right)}^{2}}~~\text{ }+\text{ }\left( {\text{ }Perpendicular\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
=~~\text{ }{{\left( {\text{ }3\text{ }} \right)}^{2}}~~\text{ }+\text{ }\left( {\text{ }4\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
= 9 + 16
= 25
Hypotenuse = √ 25
Hypotenuse = 5
Therefore , Hypotenuse of the triangle is 5 cm .
Example 2
Question: Find the base of a right triangle if the hypotenuse of the triangle is 17 cm and the perpendicular is 15 cm?
Solution: As it’s a right angled triangle, we can Apply Pythagoras theorem
\displaystyle (\text{ }Hypotenuse~){{~}^{2}}~~~=~~\text{ }{{\left( {\text{ }Base\text{ }} \right)}^{2}}~~\text{ }+\text{ }\left( {\text{ }Perpendicular\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
By putting the given values in the above relation we get ,
\displaystyle (\text{ }17~){{~}^{2}}~~~=~~\text{ }{{\left( {\text{ }Base\text{ }} \right)}^{2}}~~\text{ }+\text{ }\left( {\text{ }15\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
\displaystyle ~~~~~\text{ }289~~~~~~~~=~\text{ }(~Base\text{ })~2~\text{ }+~\text{ }225~
\displaystyle ~289~\text{ }-~\text{ }225~\text{ }=~\text{ }\left( {\text{ }Base\text{ }} \right){{~}^{2}}
\displaystyle 64~~~~~~=~\text{ }(~Base\text{ }){{~}^{2}}
Base = √ 64
Base = 8
Therefore , the base of the triangle is 8 cm .
So, this is how we can use the Pythagoras theorem to find out the unknown side of the right triangle. This theorem is not only used in geometry, this is also used in real–life scenarios as well.
Real Life Applications of Pythagoras Theorem
- We can use Pythagoras theorem to check whether a triangle is a right triangle or not.
- In ocean studies, Pythagorean formula is used to calculate the speed of the sound waves in water/sea.
- Metrological department and aerospace industry uses this theorem to determine the sound source and its range.
- In navigation this theorem is used to find the shortest distance between given points.
- In construction, architecture and planning, this theorem is used to calculate the slope of roof, dam work, drainage system, etc .
Read More – Mathematics Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development

Unleash the Power of visualization to break tough concepts
Wanna be the next Maths wizard? Discover the new way of learning concepts with real-life Visualization techniques and instant doubt resolutions.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?