Enrich your knowledge with our informative blogs
What is the structure of an atom, and how are the charge and mass calculated?
An atom is defined as the smallest unit of matter that retains an element’s all chemical properties. Atoms combine to form molecules that interact for the further formation of solids, liquids, and gases. For instance, if we talk about water, it comprises oxygen and hydrogen atoms that combine to form water molecules.
Atomic Particles
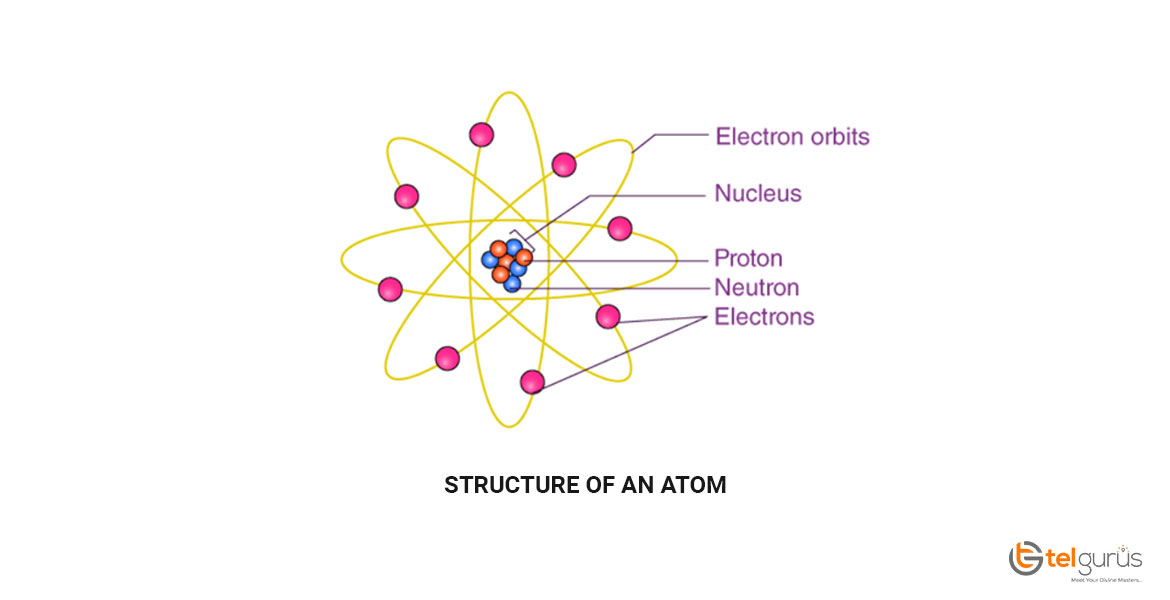
Atoms are composed of three basic particles, including neutrons, protons and electrons. The nucleus of the atoms present at the center contains the positively charged particles known as protons and no charged particles known as neutrons.
The outermost region of an atom is an electron shell that contains the electrons that are negatively charged. Atoms generally have different properties based on the number of fundamental particles and arrangements.
Structure of an atom
The atomic structure refers to the constitution of the nucleus and the electron’s arrangement around it. The structure of an atom is made up of electrons, neutrons, and protons.
The neutrons and protons make up the nucleus of an atom surrounded by electrons belonging to the atom. An element’s atomic number describes the total number of protons present in its nucleus.
Neutral atoms contain an equal number of electrons and protons. Conversely, atoms may lose or gain electrons to increase their stability or complete their octet, and the resulting charged entity is known as an ion.
The atoms of diverse elements have different atomic structures as they comprise a dissimilar number of electrons and protons. And this is the reason why different elements have unique characteristics.
Rutherford’s Structure of Atom
Rutherford proposed his own structure of the atom that includes the following.
- The atomic structure is spherical.
- The nucleus is present at the center of an atom, where most of the mass and charge are concentrated.
- Electrons revolve around the nucleus in a circular orbit identical to the way planets orbit the sun.
How is the mass of an atom calculated?
The atom’s mass is calculated by adding the number of protons with the total number of neutrons.
Mass of an atom = Total number of protons + Total number of neutrons
How is the charge of an atom calculated?
The charge of an atom is determined by the total number of electrons it loses or gains to complete its octet.
For instance, let us consider Oxygen.
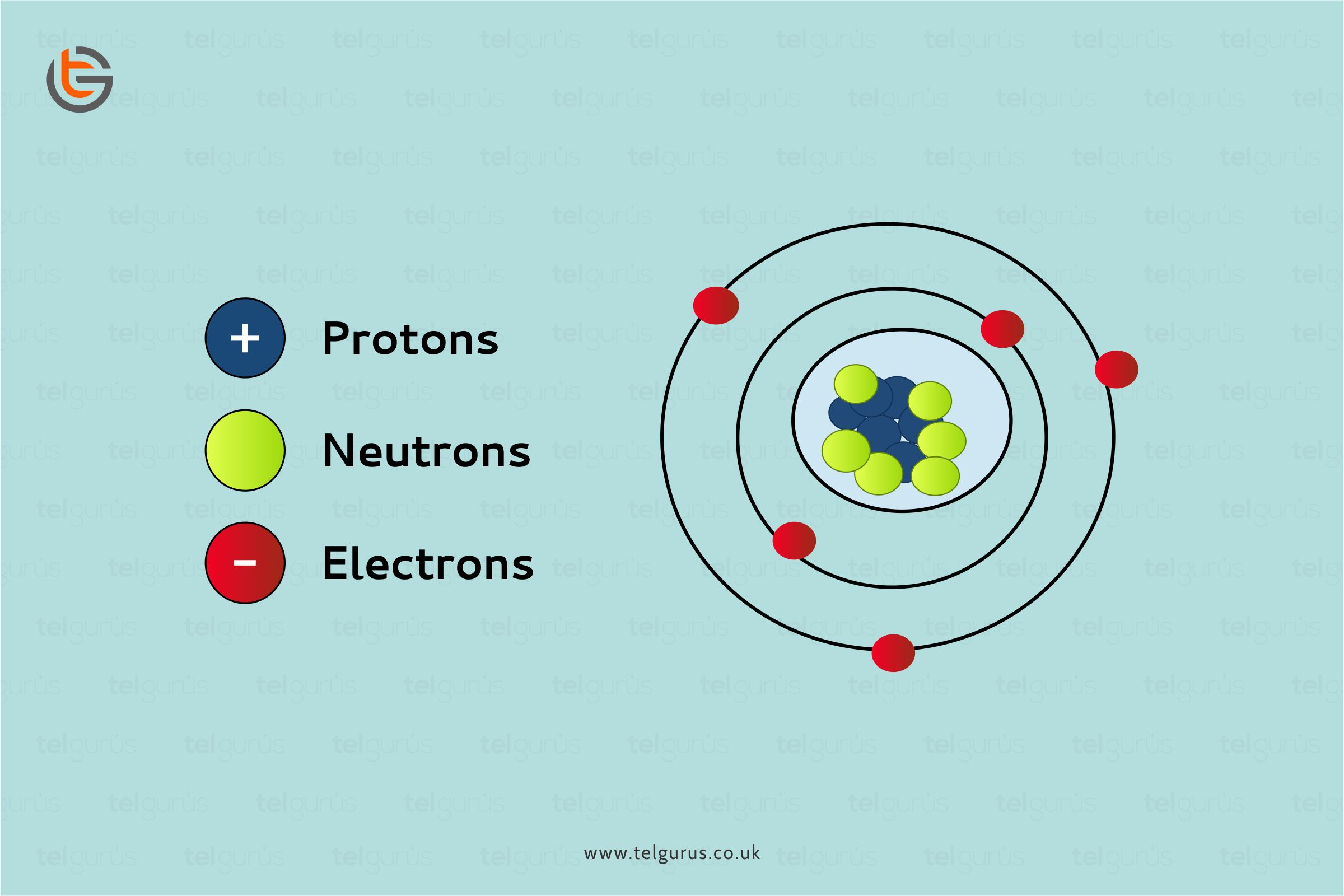
Oxygen has an atomic number of 8, and therefore the number of electrons in an Oxygen or “O” atom is also 8.
Thus, the Oxygen’s electronic configuration will be:
K=2
L=6
Where L is the outermost shell that has 6 electrons, that means the O atoms need two more electrons to complete their octet. It can also try to give away the 6 electrons in its outermost shell to complete the duplet, but that clearly requires more energy, which is why it gains 2 electrons instead of giving away 6.
When the O atom gains 2 electrons, it has two more electrons than the protons, and therefore, Oxygen has a charge of O2-.
Read More – Chemistry Questions
View More – Useful links for Your Child’s Development

Discover the exact logic behind the reactions!
Get a deeper understanding of every possible interaction between atoms, molecules and elements in an easy and fun-loving way.
Categories
Recent Posts
- List of the qualities you should look for in your tutors?
- What is the most useful formulas in math?
- Describe the process of eating to defecation of food?
- Difference between the natural and artificial active response by the immunology system.
- Explain the different circle theorems
- How are nerve cells adapted to their function?